-
Chapter 13 -- Recursion
-
Chapter 14 -- Sorting and Searching (again)
- Chapter 15 -- Data Structures (again)
-
Program 6 will be released on Friday 24 May.
-
The 100% Program 5 due date is Friday 24 May.
- Any lingering Program 4 demos will be done this week in lab.
-
There is a very good example of linked list implementation from chapter 15 of
book.
-
It's online in
102/examples/book/ch15/impllist/
-
It shows the implementation of methods for a singly-linked non-generic list.
-
It also shows implementation of an iterator for this structure.
-
We'll walk through the example in detail during lecture on Monday.
- It's directly relevant to the work you'll do in Program 6.
- On Wednesday of this week, we'll walk through the full solution to the midterm, and discuss.
-
It's a useful problem solving technique.
-
It makes some problem solutions much easier, in particular problems that in
involve accessing linked data.
- It needs to be part of a programmer's "tool bag".
-
Subdivide a large problem into separate parts.
-
Solve one simple part of the problem.
- Apply the solution to the rest of the problem.
-
Suppose we want a list elementOf method.
-
it returns true if a list contains a particular element
- it returns false if not
-
it returns true if a list contains a particular element
-
An iterative solution uses a familiar for loop, e.g.,
import java.util.*; /**** * * This class illustrates an iterative elementOf method. Compare it to the * recursive solution in ./RecursiveElementOf.java. */ public class IterativeElementOf { /** * Return true if the given element is in the given list, false if not. * The method uses a standard form of for loop to examine each element of * the list, returning true if we find the element we're looking for, false * if we run off the end of the list. */ static <E> boolean elementOf(List<E> list, E element) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { if (element.equals(list.get(i))) { return true; } } return false; } } -
A recursive solution goes like this:
-
If the list is empty, return false.
-
If the element is first in the list, return true.
- Otherwise, search the rest of the list recursively.
-
If the list is empty, return false.
-
Here's the code, which does the same work as the preceding iterative version:
import java.util.*; /**** * * This class illustrates a recursive elementOf method. Compare it to the * iterative solution in ./IterativeElementOf.java. * */ public class RecursiveElementOf { /** * Return true if the given element is in the given list, false if not. * The method uses a recursive search algorithm, consisting of the * following three steps: * * (1) If the list is empty, return false. * * (2) If the element we're looking for is the first in the list, * return true. * * (3) Otherwise, search for the element recursively in the rest of the * list, i.e, the sublist from the second through the last element. */ <E> boolean elementOf(List<E> list, E element) { /* * Step 1. */ if (list.size() == 0) { return false; } /* * Step 2. */ if (list.get(0).equals(element)) { return true; } /* * Step 3. */ return elementOf(list.subList(1, list.size()), element); } }
-
Here's a summary of the performance for the iterative and recursive solutions
to elementOf on an ArrayList and a LinkedList:
-
The iterative solution works well on an ArrayList, in O(n) time.
-
The iterative solution works poorly on a LinkedList, in O(n2) time.
-
The recursive solution works well an ArrayList, in O(n) time.
- The recursive solution works well on a LinkedList, in O(n) time.
-
The iterative solution works well on an ArrayList, in O(n) time.
-
Question: how do you explain these behaviors?
. . . thinking . . .
-
OK, so you've thought about it for a couple seconds; have a look at
Figure 1, and consider the following points:
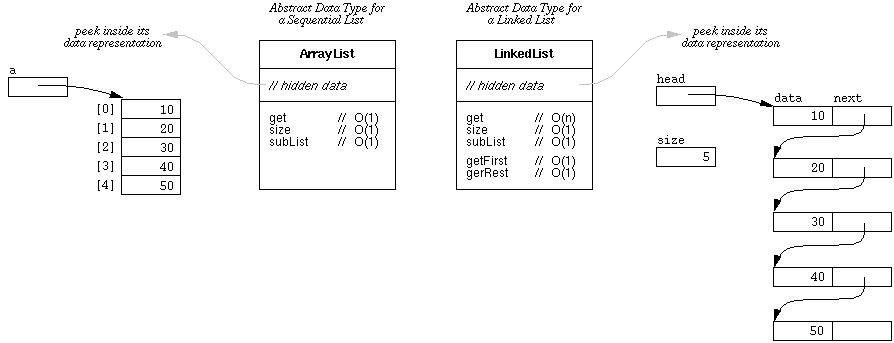
Figure 1: Abstract data types for sequential and linked lists.
-
The get(int) operation is constant on ArrayLists, whereas it's
linear on LinkedLists.
-
The getFirst() and getRest() methods are both constant on
LinkedLists. (These methods are equivalent to, respectively, get(0) and
subList(1,list.size()).)
-
The subList method is constant on both ArrayLists and LinkedLists, due to
Java's implementation of java.util.AbstractList. (Note that if
ArrayList.subList created a new array, it would be O(n). Think about what
might be going on inside the ArrayList implementation to make subList O(1).)
- Think (some more) about what these observations mean for the performance of the iterative versus recursive searches on ArrayList versus LinkedList.
-
The get(int) operation is constant on ArrayLists, whereas it's
linear on LinkedLists.