- An abstract data type defines a set of data objects and the operations that manipulate and access the data.
- What is "abstract" about an ADT is that the implementation details of the operations and the concrete representation of the data are not visible to outside users of the ADT.
- I.e., the implementation and representation details are "abstracted out" from the external ADT definition.
-
Programming languages provide a variety of built-in ADTs.
-
For example, the following is a stylized class definition for the int
ADT in Java:
abstract class int { /** * Return the sum of the given integers x and y. */ int "+"(int x, int y); /** * Return the difference of the given integers x and y. */ int "-"(int x, int y); /** * Return the product of the given integers x and y. */ int "*"(int x, int y); /** * Return the quotient of the given integers x and y. */ int "/"(int x, int y); // Other int operations ... } - This ADT defines the basic int operations that we expect from a standard programming language.
- What we cannot (and should not) see in the definition are the implementations of the operations nor the concrete representation of an int.
- These are details of the Java compiler and interpreter with which the Java programmer is not concerned.
-
It should be noted that this definition is not legal in Java because the names
of methods cannot be declared as strings such as "+".
- Also, the infix syntax of addition cannot be defined in Java; even if we could declare "+" as the name of a method, we'd have to invoke it as "+(i, j)" instead of "a + b".
- It is noteworthy that this kind of definition is legal in C++ using the C++ operator overloading feature.
-
For example, the following is a stylized class definition for the int
ADT in Java:
-
Programming languages like Java and C++ provide ADTs for all of the other
built-in data types, and for built-in data structures like arrays.
-
For example, here is a (highly) stylized definition of the array ADT:
abstract class array { /** * Construct an array from the given elements e1 through en. This method * is invoked with the syntax "{e1, ..., en}". */ array "{...}"(Object e1, ..., Object en); /** * Return the object at the ith position of the given array a. This method * is invoked with the syntax "a[i]". */ Object "[...]"(array a, int i); // Other array operations ... } - As with the int ADT, the syntax of these method definitions is not legal in Java (or even in C++).
-
The key concept of an ADT is what's important here:
- The details of method implementation are not visible to the outside ADT user.
- The details of concrete data representation are not visible.
-
For example, here is a (highly) stylized definition of the array ADT:
-
In addition to low-level built-in ADTs, the Java language has a standard
library of higher-level ADTs, called the Java Foundation Classes
(JFC).
-
For example, here is an excerpt from the JFC LinkedList class (which is
quite similar to the GeneralList ADT of Assignment 1):
abstract class LinkedList { /** * Constructs an empty list. */ public LinkedList(); /** * Returns the element at the specified position in this list. */ public Object get(int index); /** * Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the * specified element. */ public Object set(int index, Object element); // ... } - The only difference between low-level built-in ADTs and higher-level library ADTs is the syntax.
- I.e., the ADTs defined in the JFC all use standard Java method syntax.
-
Again, it's the key concepts of data abstraction that are common to Java ADTs,
both low and high-level:
- hidden method implementation
- hidden concrete data representation
-
For example, here is an excerpt from the JFC LinkedList class (which is
quite similar to the GeneralList ADT of Assignment 1):
- A list ADT is an indexable collection of objects.
- Each element in a list has a position from 0 to one less than the length of the list.
-
The specific operations provided by a list ADT vary, depending on the uses the
list is design for.
- Fundamentally, a list needs operations to add, remove, and locate elements.
- Additional operations may be provided, including sorting and content searching.
- In Assignment 1, you are being asked to implement the GeneralList ADT.
- As the writeup explains, GeneralList provides a variety of methods for storing and accessing objects in a list.
-
The diagram in Figure 1 illustrates how the storage and access methods
operate.

Figure 1: GeneralList storage and access operations.
- A copy of the Java template file GeneralList.java is attached to the notes.
-
The methods putFirst, putLast, getFirst, getLast,
removeFirst, and removeLast must each operate in O(1) time.
- This requirement means that the GeneralList implementation must provide direct access to both the front and back of the list.
- Without such direct access, an O(N) search could be required, which would violate the requirement.
-
The methods put, get, set, and remove must operate in
O(N/2) time, for N = the length of the list.
- This requirement also relies on direct access to both ends of the list.
- When one of these methods operates, it must check the given index to determine which end of the list should be used to initiate the search for the element at the index position.
- This undoubtedly requires a doubly-linked structure.
-
On a sorted list with no duplicate elements, the elementOf and
findIndex methods must operate in O(log N) time; two elements e1
and e2 are considered duplicates if e1.equals(e2).
-
This requirement means that the list must keep track internally of when it is
in a sorted state.
- Any method that affects the sorted state must change the state accordingly.
- Clearly, the sort method sets the sorted state to true.
- The put methods and some others set the sorted state to false.
-
In order to meet the O(log N) requirement, a binary search of some form
must be used.
- But note well that binary search does not operate in O(log N) time on a linked list. (Think about why this is the case.)
- This means you must use some form of parallel array to support the binary search.
- Getting this right is one of the more challenging aspects of the assignment.
-
This requirement means that the list must keep track internally of when it is
in a sorted state.
-
The sort method must operate in O(N2) time.
- This is basically an easy requirement to meet, since just about any sorting algorithm is O(N2), including the simple bubble sort below.
- Given the preceding observation about the need for a parallel array, you must be able to sort both the linked list and array in parallel, and make sure that you do not exceed the O(N2) requirement.
- In general, an array-based implementation of the list ADT is not adequately efficient.
- The main problem with using an array is that the insert operations will generally take O(N) time, where N is the length of the list.
-
For example, the following is an array-based implementation of a list
with a putFirst method that takes O(N) time:
/**** * * Class ListAsArray illustrates the O(N) running time for the * <tt>putFirst</tt> method in an array-based implementation of a list. * */ public class ListAsArray { /** * Allocate a list of the default size of 100000. */ public ListAsArray() { data = new Object[SIZE]; length = 0; } /** * Add the given element to the front of this. */ public void putFirst(Object element) { int i; // Traversal index /* * Move all of the elements to the right one position. */ for (i = length; i > 0; i--) { data[i] = data[i-1]; } /* * Put the given element in the front position. */ data[0] = element; /* * Increment the current length by 1. */ length++; } /** The array data representation */ private Object[] data; /** Current length of list */ private int length; /** The default list size */ private static final int SIZE = 100000; }- In this implementation, the variable length is a class data field used to keep track of the current length of the list.
- This is an important efficiency, since arrays must be constructed of a fixed length and we only want to move as many elements of the array as are in use at any given time.
- While this use of length does not improve the performance by an order of magnitude, it does improve it by a factor of 2.
-
Another significant problem with an array implementation is that a fixed amount
of storage must be allocated for the array in advance.
- This means that the list length is a fixed size or must be reallocated if the size is exceeded.
- Reallocation requires constructing a new array, of say twice the size as the original, and copying all of the existing elements into the new array.
- This copying operation is clearly O(N).
- The above-mentioned disadvantages of the array-based list implementation are overcome with a linked-list implementation.
- As you studied in CSC 102, a linked list uses a non-contiguous data representation, where each element contains a data value and a pointer (i.e., reference) to the next element in the list.
-
Figure 2 is a typical picture.

Figure 2: Linked list structure.
- It is the non-contiguous structure that allows elements to be put into and removed from a linked list in potentially linear time.
-
For example, here is a linked list implementation with an O(1) putFirst
method:
/**** * * Class ListAsLinkedList illustrates the O(1) running time for the * <tt>putFirst</tt> method in an linked list implementation of a list. * */ public class ListAsLinkedList { /** * Allocate an empty list. */ public ListAsLinkedList() { head = null; length = 0; } /** * Add the given element to the front of this. */ public void putFirst(Object element) { /* * If the list is currently empty, make a ListNode for the given * element and make it the first in the list. */ if (head == null) { head = new ListNode(element, null); length = 1; } /* * Otherwise, make a new node and splice it into the front. */ else { head = new ListNode(element, head); length++; } } /** Pointer to head of list */ private ListNode head; /** Current length of list */ private int length; /**** * Class ListNode is an element of linked list. A ListNode has an Object * value field and a pointer to the next node in a list. */ private class ListNode { /** * Construct a list node with the given value and next pointer. */ public ListNode(Object value, ListNode next) { this.value = value; this.next = next; } /* The data value of this node */ private Object value; /* Pointer to the next node in the list */ private ListNode next; } } - This list implementation uses a local class ListNode to define the nodes that are stored in the list.
-
A disadvantage of the linked list implementation compared to the array is that
we lose O(1) performance on methods that must access the ith position in
the list, for 0 <= i < list.length.
- Hence, there is a tradeoff between array versus linked representations
- For arrays, we get O(N) insertion at the front but, O(1) access for an arbitrary element.
- For linked lists, we get O(1) insertion at the front, but O(N) access for an arbitrary element.
- As another example of linked list implementation, here is a version of the linked list implementation presented in Section 3.2.3 of the book.
- The class header comment indicates the differences between this and the book.
-
There is no real answer to which version is "better"; they illustrate different
approaches that you can consider.
/**** * * Class BooksLinkedList is an alternate implementation of the LinkedList * example given in Section 3.2.3 of the text book. The differences between * this implementation and the book's are the following: * <ol>
- Depending on the application for which a linked list is used, it may be convenient or more efficient to have a doubly linked and/or circular structure.
-
Figures 3 and 4 illustrate these structures.

Figure 3: Doubly-linked list.
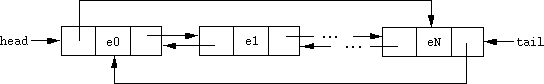
Figure 4: Circular doubly-linked list.
- When we study Chapter 7 on sorting, we will analyze sorting algorithms in some detail.
- For Assignment 1, you need to use some form of sorting.
-
Here is a version of a "bubble sort" algorithm that works on a doubly linked
list:
/** * Sort this in ascending order, based on the ordering defined by the * compareTo method applied this' elements. Return the sorted value of * this. */ public void sort() { int i, j; // Traversal indices ListNode nodeI, nodeJ; // Traversal pointers /* * Outta here if this is empty. */ if (length == 0) { return; } /* * Use a basic bubble sort algorithm. */ for (i=0; i<length-1; i++) { for (j=length-1, nodeJ=tail.prev; i<j; j--, nodeJ=nodeJ.prev) { if (((Comparable)(nodeJ.value)).compareTo(nodeJ.next.value) > 0) { swapNodeValues(nodeJ, nodeJ.next); } } } } /** * Swap the values in the given two nodes. The nodes themselves stay put. */ protected void swapNodeValues(ListNode n1, ListNode n2) { Object temp; // Temp value; /* * Use standard swap logic. */ temp = n1.value; n1.value = n2.value; n2.value = temp; } - We will study the behavior of this algorithm in lab.
-
As mentioned in the week 1 lecture, the performance of searching in a list can
be improved from O(N) to O(log N) if the list is sorted.
- The algorithm uses a "divide and conquer" strategy.
-
The idea is as follows:
- Start by looking in the middle of the list.
- If the item we're looking for is there, we're done.
- Otherwise, if the item we're looking for is less than the middle item, continue the search in the first half of the list, else in the second half.
- Continue until we either find the item or run out of list.
- This type of algorithm is typically called "binary search", since it divides the list in half at each step of the search.
-
Here is an example that illustrates both recursive and iterative binary search
algorithms on an array-based list.
/**** * * Class ListSearch illustrates the recursive and iterative algorithms for * binary search on arrays. * * * @author Gene Fisher * @version 11apr01 * */ public class ListSearch { /** * Perform a recursive binary search of the given list for the given * element, between the given start and end positions. */ protected int binarySearchRecursive(Object[] list, Object element, int startPos, int endPos) { /* * Base case is when the length of the startPos/endPos interval <= 1. * If length <= 0, return failure immediately. If length = 1, return * successfully if the searched-for element is the element at the * interval point, otherwise return failure. */ if ((startPos > endPos) || (list.length == 0)) { return -1; } if (startPos == endPos) { if (element.equals(list[startPos])) return startPos; else return -1; } /* * The recursive step is to compute the interval midpoint and then do * one of the following: * * (a) If the searched-for element is at the midpoint, return * successfully. * * (b) If the searched-for element is less than the midpoint * element, recursively search the lower half of the list. * * (c) If the searched-for element is greater than the midpoint * element, recursively search the upper half of the list. */ int midpoint = (startPos + endPos) / 2; if (element.equals(list[midpoint])) return midpoint; else if (((Comparable)element).compareTo(list[midpoint]) < 0 ) return binarySearchRecursive(list, element, startPos, midpoint - 1); else return binarySearchRecursive(list, element, midpoint + 1, endPos); } /** * Perform an interative binary search of the given list for the given * element, between the given start and end positions. Assume the list is * not null. */ protected int binarySearchIterative(Object[] list, Object element) { int startPos = 0; // Initial start position int endPos = list.length - 1; // Initial end position /* * Iterate through the list while the length of the startPos/endPos * interval is >= 1 and we haven't yet found the searched-for element. * For each loop iteration, compute the interval midpoint and then do * one of the following: * * (a) If the searched-for element is at the midpoint, return * successfully. * * (b) If the searched-for element is less than the midpoint * element, search the lower half of the list. * * (c) If the searched-for element is greater than the midpoint * element, search the upper half of the list. */ while (startPos <= endPos) { int midpoint = (startPos + endPos) / 2; if (element.equals(list[midpoint])) return midpoint; else if (((Comparable)element).compareTo(list[midpoint]) < 0 ) endPos = midpoint - 1; else startPos = midpoint + 1; } /* * Fail if we never find the element. */ return -1; } } - We will study the behavior of this algorithm in lab.
-
Look closely at line containing the compareTo invocation in the search
methods.
- In order to invoke the compareTo method, the element must be cast to the type Comparable
- This is because the general Java Object type is not itself Comparable.
- We could avoid having to use this cast by declaring the type of list element to be Comparable instead of Object.
-
Here's the advantage of declaring a data member or parameter to be Object
instead of Comparable:
- Some methods may not require Comparable.
- E.g., in the case of GeneralList, only the sorting and searching methods require compareTo, and the searching methods only require after the list has been sorted.
- Hence, if sort is never called, one could use GeneralList on objects that are not Comparable.
- So if we required the elements of GeneralList to be a list Comparable instead of the more general Object, the GeneralList ADT would be less general than it could be.
- Stacks, queues, and deques are list ADTs that have more restricted operations then general lists.
-
For a stack, the standard operations are push, pop, and top,
which add, delete, and access elements respectively.
- Push adds an element to the top (front) of the stack.
- Pop removes the most recently pushed element from the top of the stack.
- Top returns without removing the most recently pushed element from the top of the stack.
- These operations provide last-in, first-out (LIFO) access.
-
For a queue, the standard operations are enqueue, dequeue, and
front, which add, delete, and access elements respectively.
- Enqueue adds an element to the end of the queue.
- Dequeue removes the earliest queued element from the front of the queue.
- Front returns without removing the earliest queued element from the front of the queue.
- These operations provide first-in, first-out (FIFO) access.
- A deque is a double-ended queue that provides operations to enqueue and deque from both ends.
-
Stacks and queues have a wide variety of applications
- A number of interesting examples are discussed in Chapter 3 of the book.
- We will study the use of stacks and queues as the quarter progresses.