- A tree is a multi-linked data structure consisting of nodes with pointers to two or more other nodes.
- The connecting pointers between nodes are typically called tree edges.
- A tree has a distinguished node called its root to which no other node points.
- Recursively, a tree can be defined succinctly as empty, or a root node with edges to zero or more subtrees.
- There are a number of ways to depict trees in graphic form.
-
A standard textbook format shows nodes as labeled circles and edges as
connecting lines; e.g.,
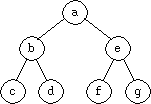
-
When we want to illustrate the implementation details of a tree, we'll draw
them in the fashion we've used for linked lists, showing the actual pointers
within the nodes, e.g.,

-
There are also a variety of ways that tree-like structures are shown in user-
oriented formats; e.g.,
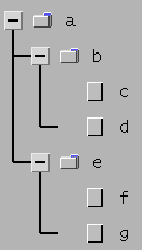
-
Lastly, when testing a program that implements tree data structures, it is
convenient to view a tree in raw string format; e.g.,
Here each vertical level of the tree is shown by indenting to the right two spaces, and (obviously) the edges are missing.a b c d e f g
-
Tree terminology is a combination of botany and genealogy.
- The topmost node of the tree is the root.
- An upper node in the tree is the parent of the nodes immediately below it, and those lower nodes are the children.
- Nodes with a common parent are siblings.
- A node is the grandparent of nodes two levels below, etc.
- Nodes with no children at the bottom of the tree are leaf nodes.
-
A path is a sequence of nodes connected by edges.
- The height of a node is the length of the longest path from the node to a leaf.
- The depth of a node is the length of the path from the root to that node
-
This terminology is illustrated in Figure 1.

Figure 1: Tree terminology.
-
The following are important tree facts.
- Every node except the root has exactly one parent.
- The root has no parent.
- There is a unique path from the root to any node.
- In tree examples above, each node had two children; such trees are called binary.
- In general, a tree node may have any number of children, from 0 to n; such trees are called n-ary.
-
Figure 2 is an example of an n-ary tree, depicting part of the CSC 103 file
directory structure.

Figure 2: Example n-ary tree.
-
The most common data representation for a binary tree is an object with three
fields: a data value, a left link and a right link:
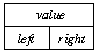
-
This can be defined in a class definition such as the following:
class BinaryTreeNode { Object value; // the value field BinaryTreeNode left; // pointer to the left subtree BinaryTreeNode right; // pointer to the right subtree } -
The data representation for an n-ary tree node code be done in a similar
fashion, with a fixed data field for each subtree pointer.
- However, if there were a potentially large number of subtrees allowed this code be unnecessary wasteful of space.
-
The typical solution is to used a linked list of subtree nodes, in a node of
this form:
where the children field points to a linked list of zero or more child subtrees and the next field points to the next child in a list of siblings.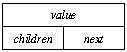
-
This form of n-ary tree node can be defined in a class definition such as the
following:
class NaryTreeNode { Object value; // the value field NaryTreeNode children; // pointer to list of children NaryTreeNode next; // pointer to next sibling } -
Figure 3 shows the concrete representation of the n-ary tree of Figure 2.
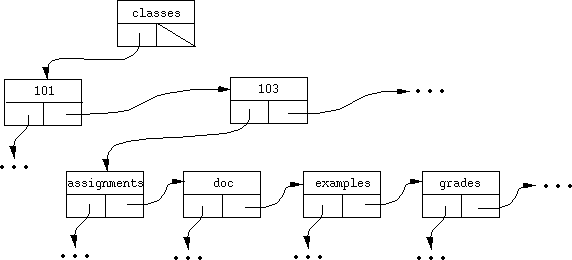
Figure 3: Concrete view of an n-ary tree..
- The attached program listing for BinaryTree.java illustrates the implementation of a basic binary tree.
-
The most fundamental operation on a binary tree is its traversal.
- Tree traversal is the process of visiting each node in the tree exactly once.
- Traversal of a two-dimensional tree structure requires a different approach than the traversal of a one-dimensional linked list we have looked at previously.
- In a linked list, we used a relatively simple for-loop to fully traverse the list.
- In a tree, a single one-dimensional for-loop won't do.
-
Here's a basic traversal algorithm for visiting all of the nodes in a binary
tree:
- If the root node of the tree is null, the traversal is done.
- Otherwise, visit the root node.
- Then recursively traverse the left subtree.
- Then recursively traverse the right subtree.
- This algorithm is called a preorder traversal, since it visits the root node first, then the left and right subtrees.
-
There are two other traversal algorithms called inorder and
postorder that work in a similar fashion, but change the point at
which the root node is visited.
-
Inorder traversal:
- Traverse the left subtree.
- Visit the root node.
- Traverse the right subtree.
-
Postorder traversal:
- Traverse the left subtree.
- Traverse the right subtree.
- Visit the root node.
-
Inorder traversal:
- The BinaryTree.findPreorder and BinaryTree.toString methods use a preorder traversal to do their work.
- A particularly useful form of binary tree is called a binary search tree.
-
A binary search tree has the following property:
For any subtree, including the full tree itself, all nodes to the left have a value less than the root and all nodes to the right have a value greater than the root.
-
For example, the following tree contains the same nodes as in the figures on
Page 1, but organized into a binary search tree:
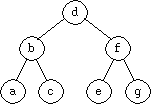
-
The most appealing property of a binary search tree is that searching for a
particular node can be performed using the following algorithm:
- If the value we're searching for is at the root, success.
- Otherwise, if the value is less than the root, search the left subtree.
- Otherwise, search the right subtree.
-
If the tree is reasonably well balanced, this algorithm can operate in
logarithmic time.
- This is the case because at each step in the search, half of the tree is eliminated from consideration.
- This is the same kind of logarithmic behavior we saw in the binary search of a linear list.
- The attached listing for BinarySearchTree.java is a sample implementation.
-
The logarithm search behavior on a binary search tree only happens when the
tree is reasonably well balanced.
- "Reasonably well balanced" means that O(N/2) of the nodes are in each half of the tree.
- The binary search tree property by itself does not guarantee a balanced tree.
-
For example, Figure 4 shows degenerate "left heavy" and "right heavy" binary
search trees.
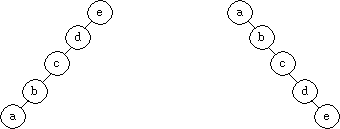
Figure 4: Left-heavy and right-heavy binary search trees..
-
In both of these trees, search time is O(N), not O(log N).
- This is because the "eliminate half the tree" step in the search algorithm ends up eliminating nothing
- So in the worst case, all N nodes of the tree must be searched to find the value at a leaf node.
-
The key to keeping a binary search tree useful is to maintain balance.
- This can be done by a global balancing algorithm, that takes any binary search tree and redistributes all of its nodes into a maximally well balanced tree.
- The problem with global balancing is that it is as expensive timewise as a complete sort.
-
A more sensible approach is to maintain balance incrementally, not
allowing the tree ever to get too far out of balance.
- Each time a node is inserted or removed from the tree, the tree balance is adjusted.
- The techniques to do this are illustrated by the AVL and red-black trees we will study next.
-
An AVL (Adelson-Velskii and Landis) tree is a binary search tree with the
following property:
For any subtree, including the full tree itself, the height of the left and right subtrees can differ by at most 1.
- This property meets the "reasonably well balanced" criterion to guarantee O(log N) searching performance.
-
Figure 5 shows two binary search trees; the one on the left is AVL, the one on
the right is not.
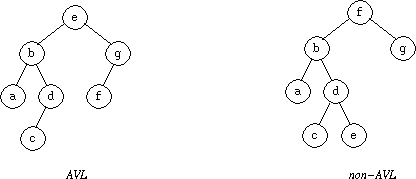
Figure 5: AVL and non-AVL trees.
- To maintain the AVL property, the tree must be rebalanced, if necessary, every time a node is inserted or deleted.
- The key to the rebalancing is a rotation operation, that grabs an unbalanced tree by its proper root node and redistributes its out-of-balance children.
-
For example, suppose we have the following AVL tree to which we add a node with
value c.
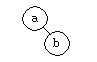
-
The steps to add the node then rotate the tree into balance are the following:
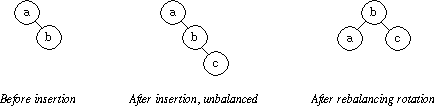
-
If we examine the possible ways that an AVL tree can go out of balance, there
are four cases, which occur when a tree rooted at node has at least two
levels:
- insertion into the left subtree of the left child of
- insertion into the right subtree of the left child of
- insertion into the left subtree of the right child of
- insertion into the right subtree of the right child of
- Cases 1 and 4 can be handled by a single rotation; cases 2 and 3 require two rotations.
- We will now examine the examples in Sections 4.4.1 and 4.4.2 of the book that illustrate the different cases.