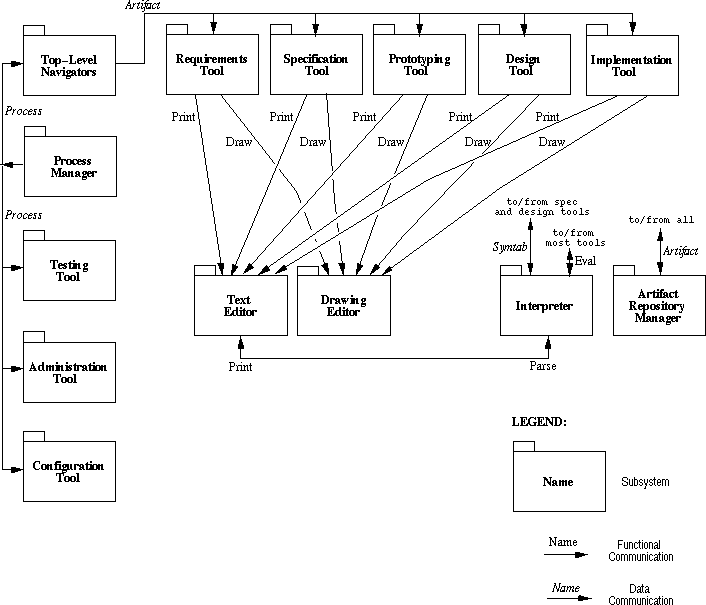
Figure 1: Inferno subsystem diagram.
- The Process Manager provides an instantiated process to the navigators and pervasive tools.
- The Top-Level Navigators provide artifacts to tools when they are launched.
- The main-line and pervasive tools manage their own specific artifacts.
- Support for displaying and editing textual representations of artifacts is provided by the Text Editor.
- Support for displaying and editing graphical representations of artifacts is provided by the Graphics Editor.
- Support for internal program representations and for execution of scripts and programs is provided by the Interpreter.
- The Artifact Repository houses the complete collection of artifacts.
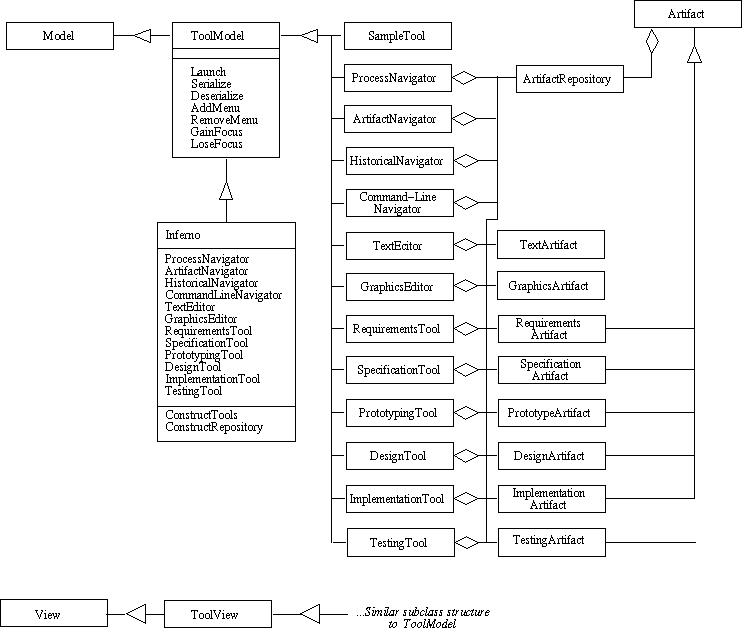
Figure 2: Inferno subsystem diagram.
- Model is the top-level parent class for all tools.
-
ToolModel is an intermediate parent class.
- Serialize transforms the internal artifact representation into a form suitable for storing on an external medium.
- Deserialize transforms a previously serialized artifact.
- AddMenu specializes the tool menubar with a tool-specific menu.
- RemoveMenu deletes a tool-specific menu.
- GainFocus gives UI focus to a tool.
- LoseFocus gives focus back to the top-level Inferno tool.
- Individual tools, including the top-level Inferno tool, inherit from ToolModel.
- The top-level Inferno tool contains a reference to all instantiated tools.
- At startup, it constructs the tools, the repository, and launches the default user tool (currently the process navigator.
The "Smaller Picture" -- Rolodex MVP Design Example
- In these notes we will examine the design of the simple rolodex system that was the subject of the formal specification primer in 508.
- In this example, we see an illustration of the design derivation step of the design process, as well as details of design refinement based on the Model View Process (MVP) design technique.
- The Model is the part of the design that is directly traceable to the specification.
- The View consists of concrete UI module(s).
- The Process is the underlying support module(s) that provide the functions that the model needs to call to get the work done.
- In the rolodex example, we'll see only model and view for now.
-
To provide support for standard designs, there are pre-defined classes Model
and View from which all model and view classes will inherit.
-
These are located in
~gfisher/projects/alpha/support/design/view.java ~gfisher/projects/alpha/support/design/model.java
-
Examples will be discussed in the context of the rolodex design later in the
notes. The rolodex project in
contains all the example files discussed in these notes.~gfisher/projects/alpha/rolodex
-
There is a sample Makefile that can be used a template for constructing Java
programs on UNIX systems; it is in
~gfisher/projects/alpha/rolodex/implementation/java/Makefile
-
These are located in
-
Details of view design are supported by the Java GUI library, known as the
Swing package.
- This package is a standard part of all Java 2 interpreters.
-
The definitive documentation source for the Java API, including the Swing
Package, is
(This Java API document was generated using javadoc, which we will use to generate our .html files stored in the project design directories.)http://www.java.sun.com/products/jdk/1.2/docs/api/index.html
- Note that we will not use the older Java AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) package; Swing supersedes AWT.
- Figures 2, 3, and 4 are snapshots of the simple rolodex tool GUI.

Figure 3: Top-Level Rolodex Interface.

Figure 4: Dialog for Adding a Rolodex Card.

Figure 5: Dialogs for Finding, Changing, or Deleting a Card.
- The following pages are the formal specification of primary module for the rolodex system.
- The module defines the main rolodex objects and the operations that appear on the Edit pulldown menu.
- Two additional modules not shown here are file.rsl and edit, which define the operations on the File and Edit menus.
-
Here is the rolodex specification module:
1 (**** 2 * 3 * Module Rolodex defines the main Rolodex object, its component objects, and 4 * the rolodex editing operations. 5 * 6 *) 7 8 module Rolodex; 9 10 export Rolodex, Card, Name; 11 12 object Rolodex is 13 components: Card*; 14 description: (* 15 A Roldex is a collection of cards. 16 *); 17 end Rolodex; 18 19 object Card is 20 components: n:Name and id:Id and age:Age and s:Sex and addr:Address; 21 description: (* 22 A Card contains the information for a person stored in a Rolodex: name, 23 id, age, sex, and street address. 24 *); 25 end Card; 26 27 object Name is string; 28 object Id is integer; 29 object Age is integer; 30 object Sex is Male or Female; 31 object Male; 32 object Female; 33 object Address is string; 34 35 operation Add 36 inputs: r:Rolodex, c:Card; 37 outputs: r':Rolodex; 38 39 description: (* 40 Add the given card to the given rolodex if a card of the same id is not 41 already there. 42 *); 43 44 precondition: 45 (* 46 * There is no card in the input Rolodex with the same id as the given 47 * input card. 48 *) 49 not CardAlreadyThere(c, r) 50 51 and 52 53 (* 54 * The values of the given card fields are valid. 55 *) 56 CardIsValid(c); 57 58 postcondition: 59 (* 60 * A card is in the output rolodex iff it is in the input rolodex or 61 * it's the new card to be added. 62 *) 63 forall (c':Card) 64 (c' in r') iff ((c' in r) or (c' = c)); 65 66 end Add; 67 68 operation Delete 69 inputs: r:Rolodex, id:Id; 70 outputs: r':Rolodex; 71 72 description: (* 73 Delete the card of the given id from the given rolodex. 74 *); 75 76 precondition: 77 (* 78 * There is a card of the given id in the input Rolodex. 79 *) 80 exists (c' in r) c'.id = id; 81 82 postcondition: 83 (* 84 * A card is in the output rolodex iff it is in the input rolodex and 85 * its id is different than the given id. 86 *) 87 forall (c':Card) 88 (c' in r') iff ((c' in r) and (c'.id != id)); 89 90 end Delete; 91 92 operation Change 93 inputs: r:Rolodex, id:Id, c:Card; 94 outputs: r':Rolodex; 95 description: (* 96 Change the card of the given id in the given rolodex to the given new 97 card. 98 *); 99 100 precondition: 101 (* 102 * There is a card of the given id in the input Rolodex, and that card 103 * is not identical with the given input card, and the given card is 104 * valid (as for Add). 105 *) 106 exists (c' in r) (c'.id = id) and (c' != c) and CardIsValid(c); 107 108 109 postcondition: 110 (* 111 * A card is in the output rolodex iff it is in the input rolodex and 112 * is not the card with the given id in the input rolodex, or it's the 113 * given input card. 114 *) 115 forall (c':Card) 116 (c' in r') iff (((c' in r) and 117 (not exists (c'' in r) (c''.id = id) and (c'' = c'))) or 118 (c' = c)); 119 120 end Change; 121 122 operation Find 123 inputs: r:Rolodex, n:Name; 124 outputs: cl:Card*; 125 description: (* 126 Find all of the cards of the given name in the given rolodex. 127 *); 128 postcondition: 129 130 (* 131 * Cards in the output list consist of those in the input Rolodex with 132 * the given name. 133 *) 134 forall (c:Card) 135 (c in cl) iff ((c in r) and (c.n = n)) 136 137 and 138 139 (* 140 * If the the output card list has more than one card, it is sorted in 141 * ascending order by card id. 142 *) 143 if (#cl > 1) then 144 forall (i:integer | (i >= 1) and (i < #cl)) 145 cl[i].id < cl[i+1].id; 146 147 end Find; 148 149 function CardAlreadyThere(c:Card, r:Rolodex)->boolean = 150 not (exists (c' in r) c'.id = c.id); 151 152 function CardIsValid(c: Card)->boolean = 153 154 (* 155 * The length of the name is <= 30 characters. 156 *) 157 (#(c.n) <= 30) 158 159 and 160 161 (* 162 * The length (i.e, numer of digits) of the id is 9. 163 *) 164 (#(c.id) = 9) 165 166 and 167 168 (* 169 * The age is a reasonable range. 170 *) 171 ((c.age >= 0) and (c.age <= 200)) 172 173 and 174 175 (* 176 * The length of the address is <= 40 chars. 177 *) 178 (#(c.addr) < 40); 179 180 end Rolodex; 181
- Applying the derivation and refinement steps of the design process presented in Lecture Notes Week 1 results in the classes that trace directly to the preceding RSL specification.
-
Here are derived and refined classes for Rolodex, Card, and Name.
1 /** 2 * 3 * Class Rolodex is the model class for the basic rolodex object, including the 4 * edit operations to add, delete, change, and find rolodex entries. 5 * 6 */ 7 8 public class Rolodex implements Model { 9 10 /*-* 11 * Public Functions 12 */ 13 14 /** 15 * Construct an initially empty rolodex. Initialize the error objects for 16 * each function that throws an exception. 17 * <pre> 18 * post: (exists (CardList cl) (this'.cl == cl) and (cl.Len() == 0)) 19 * and 20 * (exists (AddInputErrors aie) (this'.aie == aie)); 21 * and 22 * (exists (DeleteInputError die) (this'.die == die)); 23 * and 24 * (exists (ChangeInputErrors cie) (this'.cie == cie)); 25 * </pre> 26 */ 27 public Rolodex(View v) {} 28 29 /** 30 * Add the given card to this if a card of the same id is not already there 31 * and there is room for another card. 32 * <pre> 33 * pre: 34 * // There is no card in the input this with the same id as the given 35 * // input card. 36 * not CardAlreadyThere(c) 37 * 38 * and 39 * 40 * // The values of the given card fields are valid. 41 * CardIsValid(c) 42 * 43 * and 44 * 45 * // There is room for another card. 46 * (cl.Len() < MAXCARDS) 47 * 48 * post: 49 * // If none of the preconditions is violated, then a normal 50 * // postcondition holds, else an exception is thrown. 51 * if (not AddPrecondsViolated(c)) ( 52 * // A card is in the output this iff it is in the input this or 53 * // it's the new card to be added. 54 * forall (Card c') this'.In(c') iff (In(c') or (c' == c)) 55 * 56 * and 57 * 58 * // The size of this is increased by 1. 59 * (cl'.Length() == cl.Length() + 1) 60 * ) 61 * else ( 62 * // An AddInputException is thrown if any of the preconditions 63 * // is violated. The value of the exception flag is set for 64 * // each violated precondition via the ValidataAddInput 65 * // function. 66 * (throw == aie) and (aie == ValidateAddInput(c)); 67 * </pre> 68 */ 69 public void add(Card c) {} 70 71 /** 72 * Delete the card of the given id from this. 73 * <pre> 74 * pre: 75 * // There is a card of the given id in the input this. 76 * exists (Card c' | In(c')) c'.getId() == id; 77 * 78 * post: 79 * // If the precondition is not violated, then a normal postcondition 80 * // holds, else an exception is thrown. 81 * if (DeletePrecondViolated(c)) then ( 82 * // A card is in the output this iff it is in the input this and 83 * // its id is different than the given id. 84 * forall (Card c') 85 * this'.In(c') iff (In(c') and (c'.id != id)); 86 * ) 87 * else 88 * // A DeleteInputException is thrown if the precondition is 89 * // violated. 90 * throw == die; 91 * </pre> 92 */ 93 public void delete(Id id) {} 94 95 /** 96 * Change the card of the given id in this to the given new card. 97 * 98 * <pre> 99 * pre: 100 * // There is a card of the given id in the input this and that card 101 * // is not identical with the given input card, and the given card 102 * // is valid. 103 * exists (Card c' | In(c') (c'.getId() == id) and 104 * (c' != c) and CardIsValid(c); 105 * 106 * post: 107 * // If the precondition is not violated, then a normal postcondition 108 * // holds, else an exception is thrown. 109 * if (ChangePrecondViolated(c)) then ( 110 * // A card is in the output this iff it is in the input this and 111 * // is not the card with the given id in the input this, or it's 112 * // the given input card. 113 * forall (Card c') 114 * this'.In(c') iff (In(c') and 115 * (not exists (Card c'' | In(c'')) 116 * (c''.getId() == id) and (c'' == c')) or 117 * (c' == c)) 118 * ) 119 * else 120 * // A ChangeInputException is thrown if the precondition is 121 * // violated. 122 * throw == cie; 123 * </pre> 124 */ 125 public void change(Id id, Card c) {} 126 127 /** 128 * Find all of the cards of the given name in this. 129 * <pre> 130 * post: 131 * // Cards in the output list consist of those in the input this with 132 * // the given name. 133 * forall (Card c) 134 * (cl.In(c) iff (In(c) and (c.getName() == n)) 135 * 136 * and 137 * 138 * // The output card list is sorted by ascending order of card id. 139 * forall (int i, int j | 140 * (i >= 1) and (i <= cl.Length()) and 141 * (j >= 1) and (j <= cl.Length())) 142 * if i < j then 143 * cl.get(i).getId() < cl.get(j).getId(); 144 * </pre> 145 */ 146 public CardList find(Name n) {} 147 148 /** 149 * Print this to stdout. In the current design, the specs are the same as 150 * Dump below, q.v. In general, if there is a distinction between Print 151 * and Dump it is that the former produces a more nicely formated output 152 * than the latter. 153 */ 154 public void print() {} 155 156 /** 157 * Dump this to stdout by dumping each card, in List.iterator order. 158 */ 159 public void dump() {} 160 161 162 /** 163 * View Service functions. These are functions that provide data 164 * manipulation services to the views that the views cannot know how to 165 * implement. 166 */ 167 168 /** 169 * Convert to the given string to one of the Sex enumeration literals. The 170 * String value must be all lower case and only the first character is 171 * significant, i.e., "m*" or "f*". If s is not one of these values, 172 * Female is returned. 173 * <pre> 174 * post: if (s[1] == "m") then return == Male else return == Female 175 * </pre> 176 */ 177 public Sex stringToSex(String s) {} 178 179 /** 180 * Convert to the given Sex enumeration literal to an lowercase string. 181 * <pre> 182 * post: if (s == Mail) then return == "m" else return == "f" 183 * </pre> 184 */ 185 String sexToString(Sex s) {} 186 187 188 /*-* 189 * Protected Functions 190 */ 191 192 /** 193 * Validate the given card per the precondition of Add. Return the 194 * appropriately set AddInputErrors value. See the definition of 195 * AddInputErrors for further information. 196 */ 197 protected AddInputErrors validateAddInput(Card c) {} 198 199 200 /*-* 201 * Data Members 202 */ 203 204 /** Simple list rep'n of the card list */ 205 protected CardList cl; 206 207 /** Error messages for the Add function */ 208 protected AddInputErrors aie; 209 210 /** Error message for the Delerte function */ 211 protected DeleteInputError die; 212 213 /** Error messages for the Change function */ 214 protected ChangeInputErrors cie; 215 216 217 /** 218 * Auxiliary spec functions. 219 * 220 * boolean cardAlreadyThere(Card c) { 221 * not (exists (Card c' | In(c')) 222 * c'.getId() == c.getId()) 223 * } 224 * 225 * boolean cardIsValid(Card c) { 226 * // The length of the name is <= 30 characters 227 * (c.getName().Length() <= 30); 228 * 229 * and 230 * 231 * // The length (i.e, numer of digits) of the id is 9 232 * c.getId().toString.Length() == 9) 233 * 234 * and 235 * 236 * // Age is a reasonable range 237 * ((c.getAge() >= 0) and (c.getAge() <= 200)) 238 * 239 * and 240 * 241 * // Sex is valid 242 * (c.getSex() != InvalidSex) 243 * 244 * and 245 * 246 * // The length of the address is <= 40 chars 247 * (c.getAddr() < 40) 248 * 249 * } 250 * 251 * boolean addPrecondsViolated(Card c) { 252 * cardAlreadyThere(c) or (not cardIsValid(c)); 253 * } 254 * 255 * boolean deletePrecondViolated(Card c) { 256 * not (exists (Card c' | In(c')) c'.getId() == id) 257 * } 258 * 259 * boolean changePrecondViolated(Card c) { 260 * not (exists (Card c' | In(c')) (c'.getId() == id) and 261 * (c' != c)); 262 * } 263 * 264 * boolean in(Card c); 265 * // Return true if the given card is anywhere in this. 266 * Find(c) != null 267 * 268 */ 269 270 };1 /** 2 * 3 * Class Card is the model class for the Card object. A Card contains the 4 * basic information for a person stored in a Rolodex: name, SSN id, age, sex, 5 * and street address. 6 * 7 */ 8 9 public class Card implements Model { 10 11 /*-* 12 * Public Functions 13 */ 14 15 /** 16 * Construct a card with the given field values. Note that no validity 17 * checking of the given values is performed here. Rather, input value 18 * checking is done in the Rolodex::Add function, q.v. 19 * 20 * post: (this.n == n) and (this.id == id) and (this.age == age) and 21 * (this.s == s) and (this.addr == addr); 22 */ 23 public Card(Name n, Id id, Age age, Sex s, Address addr) {} 24 25 26 /*-* 27 * Field access functions. 28 */ 29 30 /** 31 * Return the name of this. 32 * <pre> 33 * post: return == n; 34 * </pre> 35 */ 36 public Name getName() {} 37 38 /** 39 * Return the id of this. 40 * <pre> 41 * post: return == id; 42 * </pre> 43 */ 44 public Id getId() {} 45 46 /** 47 * Return the age of this. 48 * 49 * post: return == age; 50 */ 51 public Age getAge() {} 52 53 /** 54 * Return the sex of this. 55 * 56 * post: return == s; 57 */ 58 public Sex getSex() {} 59 60 /** 61 * Return the name of this. 62 * 63 * post: return == addr; 64 */ 65 public Address getAddr() {} 66 67 /* 68 * Return true if this is deep equal to the given card , i.e. card all of 69 * the fields of this are equal to all of the fields of the given card. 70 * 71 * post: (this.n == c.n) and (this.id == c.id) and 72 * (this.age == c.age) and (this.s == c.s) and 73 * (this.addr == c.addr); 74 */ 75 public Boolean equal(Card c) {} 76 77 /* 78 * Print this to stdout. In the current design, the specs are the same as 79 * Dump below, q.v. In general, if there is a distinction between Print 80 * and Dump it is that the former produces a more nicely formated output 81 * than the latter. 82 */ 83 public void print() {} 84 85 /** 86 * Dump this to stdout. 87 * 88 * post: (stdout == "Name: " + n + "0 + 89 * "Id: " + id + "0 + 90 * "Age: " + age + "0 + 91 * "Sex: " + s + "0 + 92 * "Addr: " + addr + "0) 93 */ 94 public void dump() {} 95 96 97 /*-* 98 * Data Members 99 */ 100 101 /** Person name and record search key */ 102 protected Name n; 103 104 /** Person id and unique record key */ 105 protected Id id; 106 107 /** Person age */ 108 protected Age age; 109 110 /** Person sex */ 111 protected Sex s; 112 113 /** Person street address */ 114 protected Address addr; 115 116 }1 /** 2 * 3 * Class Name is the heavyweight translation of the RSL atomic object 4 * definition 5 * 6 * object Name is string; 7 * 8 * A lighter-weight class definition would have just a single public string 9 * data member. A wimped-out translation is to eliminate the mnemonic 10 * identifier "Name" entirely from the design, replacing it directly with type 11 * String. 12 * 13 */ 14 15 public class Name { 16 public Name(String value) {this.value = new String(value);} 17 public String getValue() {return value;} 18 protected String value; 19 }
- Formal preconditions and postconditions appear in the RSL specification in a reasonably standard form of predicate logic.
- When specification operations are refined into design functions, this logic must be translated into a form suitable for use in Java.
- In addition, as new functions are designed, they too should be formally specified.
- These formal specifications will subsequently be used to develop the functional test plans for the implementation.
-
Here are the conventions for formal specification language to use with Java
methods:
- The return keyword is used as a value not as a control construct.
-
The if, then and else keywords are used as expression
operators not as control constructs.
-
To be precise, the following Java
if-then-else expression
is semantically equivalent to the following standard Java expressionif X then Y else Z
X ? Y : Z
-
The following if expression
is semantically equivalent to no standard Java expression, since Java always requires the "else" part of and if-then-else expression.if X then Y
-
Therefore, the elseless if-then expression above is equivalent to the following
Java
for all types for which null is a legitimate value.X ? Y : null
-
To be precise, the following Java
if-then-else expression
- The "prime" notation is added, where x means call-state value of x and x' means return-state value of x. The prime suffix can only be appended to function parameters or to accessible data members within parameters.
-
Single-assignment bindings are provided in the following form:
name := expression
-
For example, the binding
is semantically equivalent to the following standard C/C++ macro definition:X := Y
where X must be a syntactically legal Java identifier and Y must be a syntactically and semantically legal expression within the scope where the binding appears.#define X Y
- Given the restriction noted above for the prime suffix, a bound name cannot be appended with a prime.
-
For example, the binding
-
Universal and existential quantifiers are supplied, with the following syntax:
The universal quantification form is read "for all variables declared in the simple-declarator-list such that expression1 is true, expression2 is true", and the "such that expression1 clause is optional. The existential form is read similarly.forall ( simple-declarator-list [ | expression1 ] ) expression2
exists ( simple-declarator-list [ | expression1 ] ) expression2
- The in operator is added for testing if a value is the value of at least one element of an array.
- The freed is a predicate to test if an object's storage has been freed (note that this is rarely used in Java).
-
An "idealized" Java syntax for declaring preconditions and postconditions is as
follows:
where multiple bindings are separated by semicolons.MethodDeclaration: MethodHeader PrePostConditionsopt MethodBody
PrePostConditions: Bindingsopt Preconditionopt Postcondition
For example
int F(int x, int y); pre: (x <= 0) && (y >= 100); post: return == x+y; int G(Integer i, Integer j); let: x := i + j; y := i - j; z := x * y; w := i' + j'; pre: x < y; post: (x < y) && (return == z + w); int H(Integer i, Integer j, int k) { i = i+j; return i * k; }; post: (i' == i+j) && (j' == j) && (return == i' * k); -
Since there is no existing Java compiler that will recognize this idealized
syntax, pre- and postconditions must be included in the Java comments for each
method.
- The example above for the Rolodex class shows the format of pre- and postconditions with Java method comments
- Note the use of the preformatting HTML tags surrounding the pre- and postcondition comment text (e.g., on lines 17 and 25 of the Rolodex class definitions.
- These tags ensure that pre- and postconditions are readable in the HTML files generated by Javadoc.
- Figure 6 shows a high-level class diagram for rolodex model and view classes.
- Figure 7 shows the top-level function diagram for the rolodex tool.

Figure 6: Top-level rolodex data design.

Figure 7: Top-level rolodex function design.