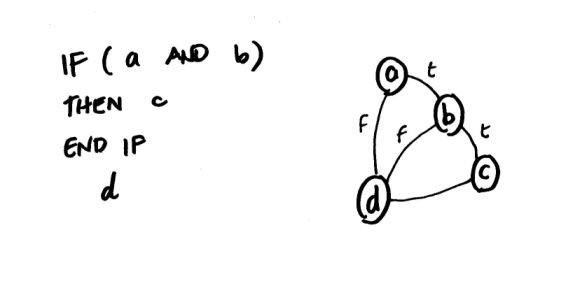
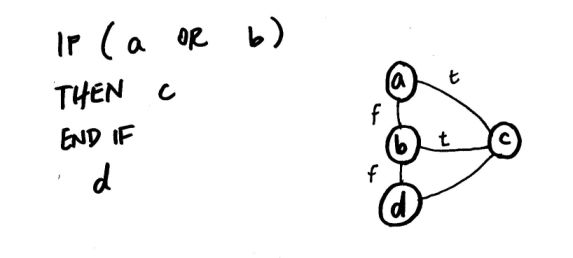
Basis Path Testing Example
Step 1: Draw the flow graph for the algorithm.
The example procedure below shows how the algorithm statements are
mapped into graph nodes, numbered on the left.
public double calculate(int amount)
{
-1- double rushCharge = 0;
-1- if (nextday.equals("yes") )
{
-2- rushCharge = 14.50;
}
-3- double tax = amount * .0725;
-3- if (amount >= 1000)
{
-4- shipcharge = amount * .06
+ rushCharge;
}
-5- else if (amount >= 200)
{
-6- shipcharge = amount * .08
+ rushCharge;
}
-7- else if (amount >= 100)
{
-8- shipcharge = 13.25 +
rushCharge;
}
-9- else if (amount >= 50)
{
-10- shipcharge = 9.95 + rushCharge;
}
-11- else if (amount >= 25)
{
-12- shipcharge = 7.25 + rushCharge;
}
else
{
-13- shipcharge = 5.25 + rushCharge;
}
-14- total = amount + tax + shipcharge;
-14- return total;
} //end calculate
Here is a drawing of the flowgraph.
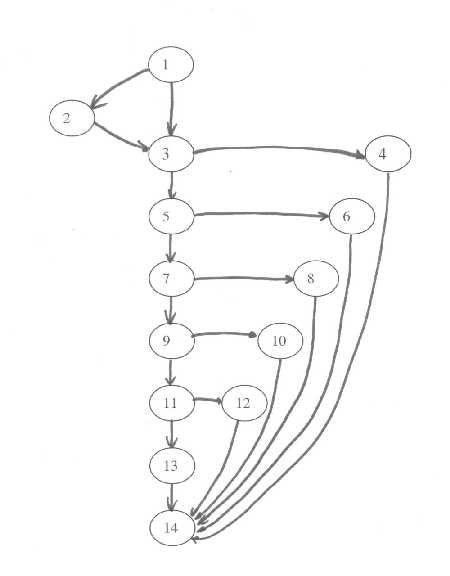
Step 2: Determine the cyclomatic complexity of the flow graph.
V(G) = E - N + 2
= 19 - 14 + 2
= 7
This tells us the upper bound on the size of the basis set. That is, it gives us the number of independent paths we need to find.
Step 3: Determine the basis set of independent paths.
Path 1: 1 - 2 - 3 - 5 - 7 - 9 - 11 - 13 - 14
Path 2: 1 - 3 - 4 - 14
Path 3: 1 - 3 - 5 - 6 - 14
Path 4: 1 - 3 - 5 - 7 - 8 - 14
Path 5: 1 - 3 - 5 - 7 - 9 - 10 - 14
Path 6: 1 - 3 - 5 - 7 - 9 - 11 - 12 - 14
Path 7: 1 - 3 - 5 - 7 - 9 - 11 - 13 - 14
Note: This basis set is not unique. There are several different basis sets for the given algorithm. You may have derived a different basis set.
The basis set "covers" all the nodes and edges in the algorithm.
Step 4: Prepare test cases that force execution of each path in the basis set.
path nextday amount expected result
1
yes
10 30.48
2
no
1500 ????.??
3
no
300 345.75
4
no
150 174.125
5
no
75
90.3875
6
no
30
39.425
7
no
10
15.975
Recommended: Use the Basis Path Worksheet to record your test cases.