-
Due 11:59PM Thurs 11 June
-
Deliverables:
-
finished implementation of requirements subset
-
JML and unit tests for 8 to 12 methods
- 100% code coverage for tested methods
-
finished implementation of requirements subset
-
Cummulative
-
Both paper and computer-based
- See the final exam overview handout for details.
-
As outlined in earlier notes, a design pattern is reusable piece of
design, based on experience that has been gained over the years by software
engineers.
-
In software engineering, the specific term "design pattern" dates back to 1995.
-
The foundational book is by Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson, and John
Vlissides.
-
This is often referred to as the "Gang of Four (GoF)" book on design patterns.
- It defined 23 specific patterns in C++ and OMT (the "Object Modeling Technique", on which UML is based).
-
This is often referred to as the "Gang of Four (GoF)" book on design patterns.
-
The original GoF defines what can be called the "classic" design patterns.
-
Some are more useful than others.
-
The patterns have also undergone refinement since original publication, in some
cases considerable refinement.
- A good deal of the basic GoF terminology has persisted in tact.
-
Some are more useful than others.
-
Hits:
-
The the gang of four coined the term, and so deserve their due in that regard.
- Several of the patterns have become well-accepted parts of the software design vocabulary, even if the details of the patterns have evolved.
-
The the gang of four coined the term, and so deserve their due in that regard.
-
Misses:
-
There is not a good high-level organizational framework for the patterns,
particularly in terms of the size and scope of the different patterns.
-
There are a a number of fundamental and frequently-used patterns that they did
not cover at all.
-
Some details of the C++ presentation are somewhat or entirely inapplicable to
languages like Java and C#.
-
For Java in particular, a few of the patterns have been largely subsumed by the
interface feature.
- Some of the patterns really aren't that useful anymore.
-
There is not a good high-level organizational framework for the patterns,
particularly in terms of the size and scope of the different patterns.
-
Multi-class patterns defined as UML class diagrams.
-
Multi-package patterns defined as UML package diagrams.
-
Single-class patterns defined as the API of one class or interface.
-
A piece of behavior defined in a function or dataflow diagram.
- Diagrams have explanatory UML comments, or accompanying prose.
-
Creational Patterns
-
Singleton -- Ensure that a class only has one instance, and
provide a global point of access to it.
-
Factory Method -- Define an interface for creating an object,
but let subclasses decide which class to instantiate.
-
Abstract Factory -- Provide an API for creating families of
related or dependent objects, without specifying the concrete class instances.
-
Builder -- Separate the construction of an object from its
representation, so that the same construction process can create different
representations.
- Prototype -- Provide new objects by copying an prototypical example.
-
Singleton -- Ensure that a class only has one instance, and
provide a global point of access to it.
-
Structural Patterns
-
Adapter -- Adapt the interface provided by one class to suit
the needs of a third class that needs a different interface.
-
Facade -- Provide a unified interface to a set of interfaces
in a subsystem.
-
Decorator -- Add properties or behaviors to a class by
enclosing it in another class that implements the properties or behaviors.
-
Bridge -- Separate an abstraction from its implementation, so
the two can be independently specialized.
-
Composite -- Define objects so that composite and atomic
instances can be treated uniformly.
-
Flyweight -- Use sharing to support large numbers of fine-
grained objects efficiently.
- Proxy -- Provide a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it.
-
Adapter -- Adapt the interface provided by one class to suit
the needs of a third class that needs a different interface.
-
Behavioral Patterns
-
Iterator -- Provide a way to access the elements of an
aggregate object sequentially, without exposing its underlying representation.
-
Mediator -- Define an object that encapsulates how a set of
objects interact, without having the mediated set of objects refer to one
another explicitly.
-
Chain of Responsibility -- Avoid coupling the sender of a
request to its receiver by giving more than one object a chance to handle the
request.
-
Command -- Encapsulate a request as an object, thereby
allowing clients to be parameterized with different requests, queue or log
requests, and support undoable operations.
-
State -- Distribute state-specific logic across multiple
classes that represent and object's state.
-
Memento -- Without violating encapsulation, provide for the
storage and restoration of an object's state.
-
Observer -- Define a one-to-many relationship among objects,
so that when an observed object changes state, all of its observers are
notified so they can update themselves.
-
Template Method -- Define main steps of an algorithm in a
superclass, deferring the definition of some steps to subclasses.
-
Strategy -- Encapsulate alternative algorithmic strategies in
separate classes that each implement a common operation.
-
Visitor -- Let a new operation be defined without changing
classes of the elements on which it operates.
- Interpreter -- Given a language, define a representation for its grammar along with an interpreter that uses the representation to interpret sentences in the language.
-
Iterator -- Provide a way to access the elements of an
aggregate object sequentially, without exposing its underlying representation.
-
Model/View -- Organize a set of classes into those that
provide the basic data model and those that provide user-level views of the
data.
-
Client/Server -- Define the responsibilities and
interconnection between a server that operates remotely from its clients.
-
Data Instantiation -- Specify where in the hierarchy of data
composition instantiated objects are created.
-
Data Communication -- Specify data communication as parametric
or persistent storage access.
-
Push/Pull -- Define provider and consumer classes, and define
the direction of data exchange.
-
Wrapper -- Isolate the platform-dependent services in well-
encapsulated classes, and provide generic platform-independent interfaces to
them.
- Design by ContractTM -- Define preconditions and postconditions for all methods, requiring that preconditions be enforced by callers or callees.
-
What follows are some examples of classic design pattern usage relevant to CSC
307.
- The examples illustrate the use of the patterns with Java foundation and GUI classes, with UML diagrams and code excerpts as applicable.
-
A typical implementation of this pattern uses a static class boolean variable
to record if an instance of the single object has yet been created.
-
The implementation also provides a singleton creation method that behaves as
follows:
-
If no instance has yet been created, call the constructor, save the result, set
the boolean is-created flag, and return the object.
- If an instance has already been created, just return it.
-
If no instance has yet been created, call the constructor, save the result, set
the boolean is-created flag, and return the object.
-
An alternative implementation is to have a singleton constructor throw an
exception if its already been called, e.g.,
public class Singleton { public Singleton() throws AlreadyInstantiatedException { if (isInstantiated) { throw new AlreadyInstantiatedException(getClass().getName()); } isInstantiated = true; } protected static boolean isInstantiated = false; } public class AlreadyInstantiatedException extends RuntimeException { public AlreadyInstantiatedException(String targetClass) { this.targetClass = targetClass; } public String targetClass; } -
A more benign approach to enforcing singleton behavior is to define a
class with a private constructor, and an accesser method that calls the
constructor at most once, e.g.,
public class Singleton { private Singleton() { . . . } public static Singleton getInstance() { if (instance == null) { instance = new Singleton(); } return instance; } protected static Singleton instance; } -
There may be cases where a Singleton pattern is used implicitly in a design,
without enforcement.
-
This can occur when there is no reason to have more than
a single instance of a class, but there is no particular harm in having
multiple instances.
-
In such cases, there may be no need to enforce Singleton behavior, but rather
call constructor once only by design convention.
- This approach happens regularly in the CSC 307 example project.
-
This can occur when there is no reason to have more than
a single instance of a class, but there is no particular harm in having
multiple instances.
-
A factory method is like a constructor, but it can return objects of different
types.
-
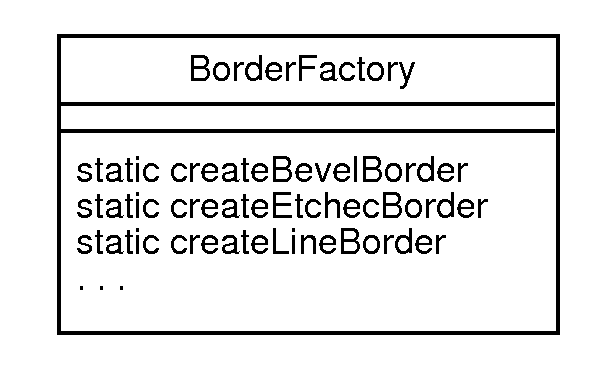
An archetypal example of a factory class is javax.swing.BorderFactory.
-
It's described in the JFC documentation as a "Factory class for vending standard
Border objects."
-
The documentation goes on to say "Wherever possible, this factory will hand out
references to shared Border instances."
-
It has create methods that return a variety of different frame JComponent
borders.
-
A value added of create methods is that they deal with Border constructor
parameters so the factory user does not have to.
-
E.g.,
-
It's described in the JFC documentation as a "Factory class for vending standard
Border objects."
-
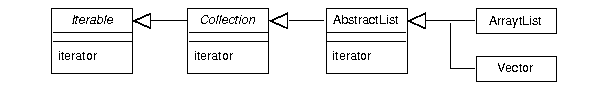
Another example of a factory method in JFC is
java.util.Iterable.iterator,
-
The iterator factory method constructs an Iterator object and
returns it; it's not a constructor.
-
The method determines which subclass of Iterator to create, hiding some
of the construction details from the user.
-
The value added over constructor is that it creates an iterator for an in-hand
collection.
-
The iterator method is defined in the Iterable interface,
inherited by the Collection interface, implemented in the
AbstractList class, and available in (but not re-implemented in)
AbstractList's extensions:
-
The iterator factory method constructs an Iterator object and
returns it; it's not a constructor.
-
The purpose of builder is to "Separate the construction of an object from its
representation".
-
This is useful when the construction of an object is complex, involving
extensive data analysis or validation.
-
For example, the construction of an object that takes a large amount of textual
input from a user may involve parsing the input, which includes ensuring
that the input data is grammatically correct.
-
In such cases, the constructor creates a shell for the object rather than
performing the parsing.
- It then calls the builder to populate the shell.
-
For example, the construction of an object that takes a large amount of textual
input from a user may involve parsing the input, which includes ensuring
that the input data is grammatically correct.
-
There are some builder class examples in JFC, including DocumentBuilder
and ProcessBuilder.
- In the CSC 307 version of the mvp.View class, the compose methods follows the builder pattern at the method level, separating the construction of a GUI object and the specific details of its layout.
-
This pattern is related to builder in that the construction of an object may
involve a lot of work.
-
In the case of the prototype pattern, the construction process can avoid
performing a large amount work by making a copy of some static
prototypical data, and then modifying the data as necessary.
-
The classic prototype pattern specifies that a clone method is defined
to provide the prototypical copy.
-
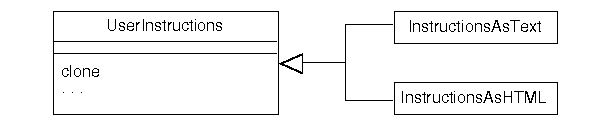
An example for 307-like projects could be in a set of classes that provide
user-level instructions in plain text, HTML, or possibly other formats.
-
A prototype class defines the raw instruction context in textual form.
-
The specializing classes clone the text and possibly add to it to produce the
desired format.
-
Here's a summary UML diagram:
-
A prototype class defines the raw instruction context in textual form.
-
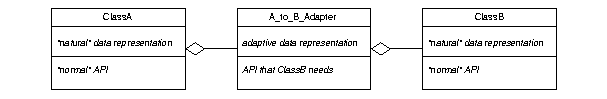
This pattern allows one class to use the services of another, when the serving
class does not provide the API the first class wants or needs.
-
To do the adaptation, a third adapter class is used to covert a provided
API into a desired API.
-
Generically, the pattern looks like this:
-
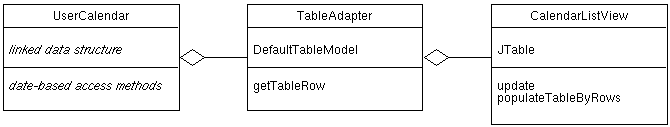
A very good example of adaptors we've seen in 307 is the use of
DefaultTableModel as an adaptor between a model class that does not
provide the API that a JTable view class needs.
-
The "natural" representation for the UserCalendar is a linked and hashed
data structure, and it's normal API provides access to the calendar by lookup
on dates and other calendar item fields.
-
The natural representation for a tabular view using Java Swing is a
JTable, to which the UserCalendar API is ill-suited.
-
The TableAdapter class uses a javax.swing.DefaultTableModel to
adapt the UserCalendar to the CalendarListView.
-
The getTableRow method extracts data from the calendar, providing it to
the view a row at a time.
- The view has a JTable, which it it populates row-wise when its update method is called.
-
The getTableRow method extracts data from the calendar, providing it to
the view a row at a time.
-
The "natural" representation for the UserCalendar is a linked and hashed
data structure, and it's normal API provides access to the calendar by lookup
on dates and other calendar item fields.
-
A facade is a way to consolidate the services provided by a multi-class
subsystem into a single.
-
Typically, the original subsystem will not have been written to be reused as a
single service.
-
In particular, methods that would go in its API may have fewer explicit
parameters than might be desired.
-
An often-cited example of the facade pattern is one for a programming language
compiler that is not intended for programatic reuse.
-
The facade defined a Compiler class, which interfaces to the various
internal components of the compiler.
- This facade can be used in an IDE program, to treat the compiler as a black box.
-
The facade defined a Compiler class, which interfaces to the various
internal components of the compiler.
-
For 307 projects, a facade could provide programmatic access to the entire
application, for scripting purposes, for example.
-
E.g.,

-
The calendar tool provides all of the functionality offered by the facade, but
does so in methods that do not have the convenient parameterization and return
values provided by the facade methods.
- In addition, the facade provides a full set of scripting methods in a single class, where in the Calendar Tool application these methods are spread across multiple classes.
-
E.g.,
-
Another example is programmatic access to a drawing editor, that was designed
originally for access by an end user through a mouse interface, e.g.,
where again the value-added provided by the facade is parameterized versions of extant methods, and the collection of all the tool's user-accessible methods into a single class.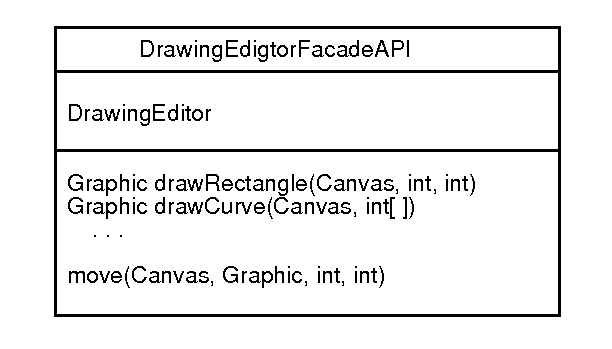
-
A decorator pattern adds features or behaviors to a class by having the
decorated class be a component, instead of having the decorated class inherit
from the decorator.
-
In this way, not all instances of the class need have the decorations.
-
An example cited in GoF are decorators for GUI classes, i.e., JComponents
in Java.
-
The decorations are features such as borders and scrollbars.
-
Rather than having these features be inherited from JComponents, they are
added as decorations around extensions of JComponents.
- This is in fact the way these features are designed in Swing.
-
The decorations are features such as borders and scrollbars.
-
This pattern is essentially what interfaces and abstract classes are all about
in Java.
- Namely, the bridge pattern separates concrete implementations from abstract definitions.
-
This pattern allows an object that can be either composite or atomic to be
treated uniformly.
-
A simple and illustrative example is the typical design of a node in a tree.
-
An interior tree node, i.e., one with children, is conceptually composite.
-
A leaf node is conceptually atomic.
- Defining a single class for both interior and leaf nodes is an application of the Composite pattern that allows the nodes to be treated uniformly in tree-manipulation methods.
-
An interior tree node, i.e., one with children, is conceptually composite.
-
This pattern is aimed at efficient use of storage for objects that are composed
of many small parts.
-
A typical application of flyweight is for string-based data, where any
character or string of characters can have attributes.
-
Having each character being represented by a heavy-weight class object would be
quite inefficient.
-
Instead, the underlying data are represented as a plain string, with flyweight
classes that represent attributes for character sequences.
- The sequences are represented as ranges of character positions in the strings, or pointers into the string.
-
Having each character being represented by a heavy-weight class object would be
quite inefficient.
-
A proxy class provides a place holder for a service-providing class that may
not yet exist.
-
If an instance of the service-provider does not exist, the proxy does the
instantiation when the service-consumer asks for one.
- In this way, the service-provider is instantiated on demand, transparently to the service-consumer.
-
E.g.,

-
The DocumentEditor uses the GraphicContent interface to perform
operations on the graphic content represented as images.
-
The TGraphicImageProxy implements the interface, and fetches image data
from a file if the data have not yet been fetched, or uses cached image data if
available.
- The fetching/caching behavior of the proxy is transparent to user of the GraphicContent interface.
-
The DocumentEditor uses the GraphicContent interface to perform
operations on the graphic content represented as images.
- For Java, the original GoF Iterator pattern has been fully subsumed by the design of iterators in Java and JFC.
-
A mediator class is the parent to other sibling classes that need to
communicate with one another.
-
Rather than having the siblings refer directly to one another, they each refer
to the mediator, who forwards the communication request.
-
The mediator pattern is used extensively in the 307 Calendar Tool example.
-
For example, the top-level CalendarTool model class instantiates
sub-models and saves a reference to all of them.
-
It also provides get methods to access the sub-model references.
-
In this way, the sub-models themselves do not have direct reference to one
another
-
Rather, each sub-model has a reference to its parent CalendarTool class,
which acts as a mediator of all the sub-models.
- Any sub-model accesses one of its sibling sub-models through the access methods provided by the mediating CalendarTool model above.
-
For example, the top-level CalendarTool model class instantiates
sub-models and saves a reference to all of them.
-
This pattern defines how a request can be satisfied by multiple handlers,
without the requester knowing exactly who does the satisfying.
-
The requester sends the class to the first potential provider; if that provider
cannot satisfy the request, it forwards it to others, who eventually will
handle it.
-
E.g.,
Client Handler1 ... -------- Info1 nextHandler: -------- request(Info) -------- Handler <----- Handler1 ... Handlern Info <----- Info1 ... Infon
-
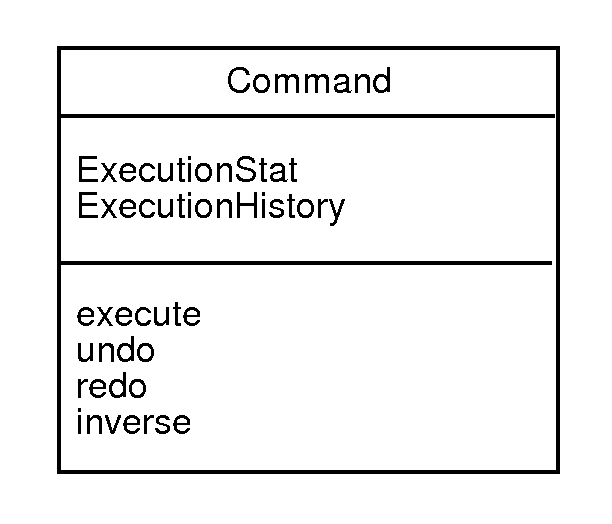
A command is a heavy-weight class for encapsulating the operational behavior of
a method.
-
The class contains meta-information about command execution, such as the value
of past parameters, or the values of past executions.
-
A very typical use of the Command pattern is for undoable operation, where the
Command class has stored data or other information necessary to support
undo/redo.
-
Undo/redo can be supported by an execution history that contains copies of
previous states, or an inverse command method that computationally undoes the
effect of a command execution.
-
Generically, the a command class looks like this:
-
A State class provides an abstraction used in a state-base design.
-
For example, the design of a communication system is based on states like
IDLE, ACTIVE, DATA_WAITING, etc.
-
A State class defines common methods that each specific state must
implement, and the value of the state.
-
The extending classes implement the methods, and set the state value as
appropriate.
-
E.g.,
class Data { DataState state; public void handle() { state->handle(...) } } interface DataState { void handle(...); } class IdleState implements DataState { void handle(...); } class ActiveState implements DataState { void handle(...); } class WaitingState implements DataState { void handle(...); } -
This pattern is an object-oriented version of a state-based design that
typically looks like the following in non-object-oriented languages, such as
plain C:
class Data { Enum state ... ; public void handle() { switch (data.state) { case IDLE: handleIdle(...) case ACTIVE: handleActive(...) case WAITING: handleWaiting(...) } } } - The pattern uses inheritance and polymorphism in a standard way to better modularize the design.
-
This pattern is related to State.
-
A Memento class represents parts of a state that need to be written to and
retrieved from persistent storage.
- Typically, only a subset of the State's components are stored in the Memento.
-
The original GoF Observer pattern has been fully subsumed by the
Observer/Observable pattern in Java JFC, and comparable patterns in
the libraries of other languages
- Discussion of the observer/observable pattern is on previous lecture notes and the examples.
-
This is a very general pattern for distributing method behavior in an
abstraction hierarchy.
-
The higher-level Template Method defines a fixed signature and defines some
general method behavior, i.e., an algorithmic skeleton.
-
Overloads of the Template Method further specialize the behavior based on the
design of the class in which they reside, in particular to implement substeps
that the skeleton does not implement.
-
A typical use of this pattern in Java is when sub-class constructors call their
parent constructor using super.
-
The parent constructor can be seen as a template initializer, that initializes
the data common to the sub-classes.
- Each sub-class constructor uses the parent initialization template, and then adds its own initialization as necessary.
-
The parent constructor can be seen as a template initializer, that initializes
the data common to the sub-classes.
-
This is also a very general pattern that has been very largely subsumed by the
interface concept of Java.
- The idea of a strategy is to provide an abstract API for operations that can be concretely implemented in a number of different ways, which is fundamentally the relationship between an interface (which specifies the strategy abstractly) and the implementing classes (which concretely implement the strategy).
-
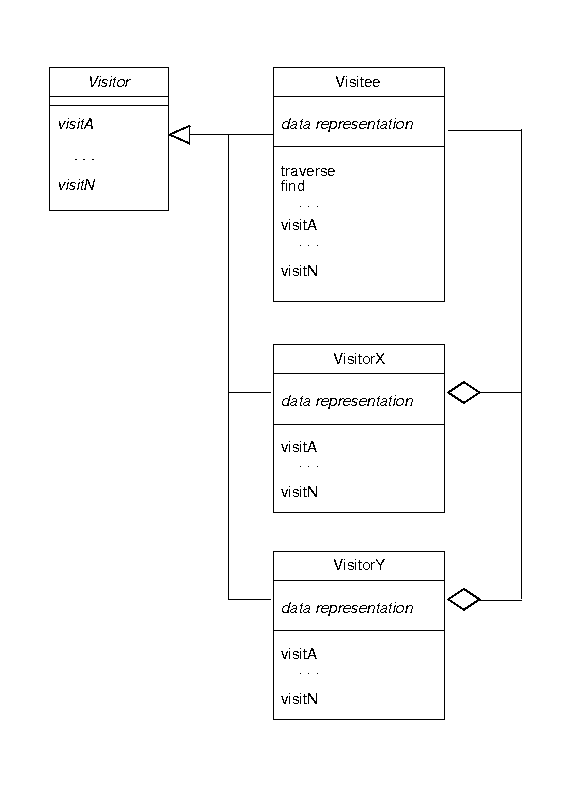
The Visitor pattern allows classes that need to perform operations on some
encapsulated data to perform those operations without changing the original
encapsulation.
-
Two class hierarchies are defined
-
A base class hierarchy that constructs all data and its elements.
- A parallel visitor class hierarchy, that provides operation on the elements, without constructing the original overall hierarchy.
-
A base class hierarchy that constructs all data and its elements.
-
A generic datagram for the pattern looks like this:
-
The Visitor interface defines the methods that are invoked at each
stage of a visitation.
-
The Visitee class defines the encapsulated data representation for the
data to be visited, a traverse to perform an overall visitation, and
any other methods that may be useful to concrete visitors, such as a
find.
-
Visitee also implements the visit methods for its on
traversal purposes.
- Concrete visiting classes, such as VisitorX and VisitorY will perform specialized forms of visitation; to do so, they
-
The Visitor interface defines the methods that are invoked at each
stage of a visitation.
-
A specific use of the Visitor pattern is often applied to tree-structured data,
e.g.,
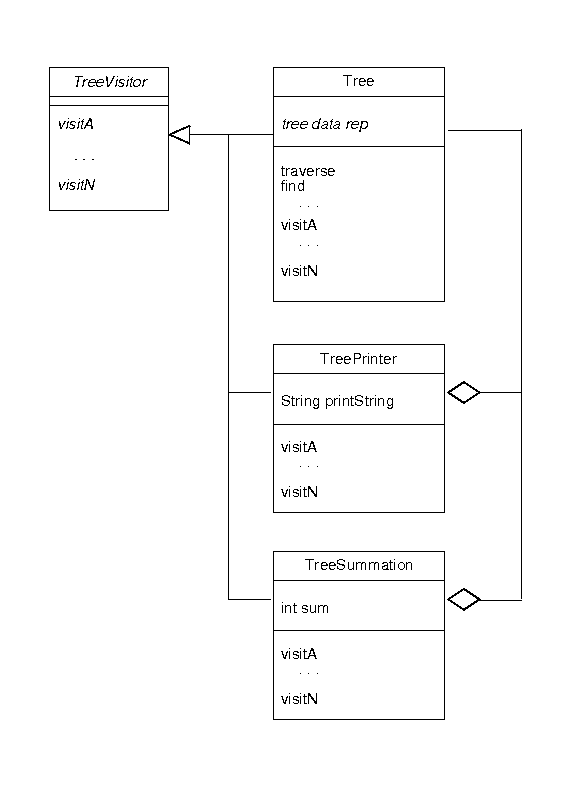
-
A parent tree class defines the tree structure, traversal method, and generic
(may be no-op) visiting methods for each type of node.
-
The specializing children define different actions, that rely on the traversal
to perform their work.
-
E.g., the TreePrinter has a string that represents the print result,
and implements the visiting methods to concatenate the print name of each node
to the print string.
- The TreeSummation class has an integer to which the traversal methods add the numeric value of each node.
-
A parent tree class defines the tree structure, traversal method, and generic
(may be no-op) visiting methods for each type of node.
-
This is by far the broadest of the original GoF patterns.
-
The aim is to define the general pattern of a language interpreter, consisting
of a lexical analyzer, parser, and interpreter.
-
In actual use, applying this pattern takes a substantial amount of knowledge,
that cannot be represented in a simple pattern definition.
-
In this sense, Interpreter stands apart from the other patterns in its scope.
- Implementors of an Interpreter patter, or closely related Compiler pattern, need to understand regular expressions, context-free grammars, and programming language semantics.
-
In this sense, Interpreter stands apart from the other patterns in its scope.
-
E.g.,
lexer ----> Parser ----> Interpreter
-
Several of the original patterns defined by the GoF have stood the test of time
well, some less so.
- As outlined above, there are other design patterns that are not part of the original GoF catalog, examples of which follow.
- Previous lecture notes and examples have covered the model/view pattern in detail.
-
The client-server pattern is generally implemented in Java using RMI --
remote method invocation.
-
This has been used in a number of 307 projects.
- A simple example of RMI-based client/server design and implementation is in 307/examples/rmi
-
A number of the patterns discussed above have dealt with data instantiation in
different ways.
-
In the pattern examples, as well as in other 307 examples, there are the
following three underlying patterns of data instantiation:
-
Instantiate up-front; e.g., the way sub-model and
sub-view classes are allocated and referenced in Calendar Tool managerial
classes.
-
Instantiate on-demand and cache; e.g., the way a
singleton class can be allocated, and the way the CalendarTool could work if
up-front allocation was deemed too costly, i.e., there was a large lag time at
tool start up.
- Instantiate on demand and destroy (garbage collect); e.g., the way transient viewing classes are allocated in the Calendar Tool, where the view data are computed dynamically every time a display is updated.
-
Instantiate up-front; e.g., the way sub-model and
sub-view classes are allocated and referenced in Calendar Tool managerial
classes.
-
As with data instantiation, a number of the patterns discussed above have dealt
with data communication in different ways.
-
Throughout the pattern examples, and in the 307 calendar tool examples, there
are the following two underlying patterns of data communication:
-
parametric -- data are sent to methods as parameters,
and provided as return values
- persistent data -- data are accessed by methods from data fields, and provided as modified data fields
-
parametric -- data are sent to methods as parameters,
and provided as return values
-
A generic example of these two patterns is the following, concrete examples of
which are found throughout the 307 examples:
public class Data { /** * Compute using current data field values and storing results in the data * fields. */ void compute() { System.out.println("x,y=" + this.x + "," + this.y); } /** * Compute using parameters and returning results. As a side effect, data * fields are set. */ Data compute(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; System.out.println("x,y=" + this.x + "," + this.y); return this; } void setX(int x) { this.x = x; } void setY(int y) { this.y = y; } /** * Perform a persistent-data computation by setting the class fields and * calling the field-accessing compute method. */ static void useWithSets() { int a = 1; int b = 2; int c = 3; int d = 4; Data data = new Data(); data.setX(a); data.setY(b); data.compute(); data.setX(c); data.setY(d); data.compute(); } /** * Perform a parametric computation by setting method-local variables, and * calling the parametric compute function. */ static void useWithParms() { int a = 1; int b = 2; int c = 3; int d = 4; Data data = new Data(); data.compute(a,b).compute(c,d); } public static void main(String[] args) { useWithParms(); useWithSets(); } protected static int x; protected static int y; }
-
This pattern is defined in terms of two classes -- a producer and a
consumer.
-
These two classes determine who initiates the data exchange, which can be
defined as data-driven versus demand-driven patterns.
-
E.g.,
__________________ __________________ Producer Consumer __________________ __________________ Data Data __________________ __________________ Data provideData acceptData(Data) __________________ __________________
-
In a demand-driven pattern, the Consumer calls Producer.provideData
for a PULL.
-
In a data-driven pattern, the Producer calls Consumer.acceptData() for
a PUSH.
-
Direction determiners include:
-
Which side is the asynchronous initiator -- data- versus demand-driven.
- The level of trust between the sides -- e.g., AJAX is always PULL.
-
Which side is the asynchronous initiator -- data- versus demand-driven.