-
Better understanding of software.
-
Precise communication among developers.
-
Basis for thorough testing.
-
Basis for formal verification (when appropriate).
-
Basis for automatic programming (dream on).
-
Here's a motivational bottom line:
-
Suppose your boss says:
I want you to do whatever it takes to build me software of the best possible quality, that has the smallest possible likelihood of failing.
- For some academics and software professionals, formal specification is a key part of addressing a mandate like this.
-
Suppose your boss says:
-
As model object and operation definitions take shape, we are ready to formalize
the definitions fully.
-
The formal technique we will use in 307 is based on operation
preconditions and postconditions.
-
A precondition is a predicate (i.e., boolean-valued expression) that is true
before an operation executes.
-
A postcondition is a predicate that is true upon completion of an operation.
- Since pre- and postconditions are predicates, this style of formal specification called predicative.
-
A precondition is a predicate (i.e., boolean-valued expression) that is true
before an operation executes.
-
The pre- and postconditions are used to specify fully what the system does,
including all user-level requirements for the system.
-
This formal specification is part of the overall requirements specification
process we're following, with these steps:
-
gather user-level requirements via usage scenarios
-
identify objects and operations
-
formalize operations with pre- and postconditions
-
refine user-level requirements based on formal specs
-
refine formal specs based on user-level refinements
- iterate steps 1-5 until done
-
gather user-level requirements via usage scenarios
-
The "until done" step involves two levels of validation.
-
First, we must validate that the specified system is complete and consistent
from the end user's perspective.
-
That is, the system meets all end-user needs and does so in a way that is
wholly satisfactory to the end user.
- This is accomplished by continued consultation with the end user.
-
That is, the system meets all end-user needs and does so in a way that is
wholly satisfactory to the end user.
-
The second level of validation involves completeness and consistency from a
formal perspective.
-
This can be accomplished in a number of ways.
-
In the case of mechanized specification languages, such as Spest, some
completeness and consistency checking is done using a computer-based analyzer.
-
Another valuable validation technique is peer review via formal walk-throughs.
-
Also, there are techniques for formal specification testing, including the
postulation and proof of putative theorems.
-
Such theorems define properties of the system that we expect to be true, and
which can be proved true formally with respect to the pre- and postconditions.
- We will discuss putative theorems briefly in 307, but not use them.
-
Such theorems define properties of the system that we expect to be true, and
which can be proved true formally with respect to the pre- and postconditions.
-
This can be accomplished in a number of ways.
-
First, we must validate that the specified system is complete and consistent
from the end user's perspective.
-
In developing any formal software specification, it is useful to observe the
following two maxims:
-
Nothing is obvious.
- Never trust the programmer.
-
Nothing is obvious.
-
The first maxim relates primarily to user-level requirements.
-
It is often easy to think that a requirement is sufficiently obvious that it
need not be stated formally.
-
The problem with this thinking is that one person's obvious is not always the
same as another's.
- To ensure that a specification is sufficiently precise, stating the "obvious" is necessary.
-
It is often easy to think that a requirement is sufficiently obvious that it
need not be stated formally.
-
The second maxim is necessary to avoid nasty surprises in an implementation.
-
In many cases, we might consider an application to be sufficiently simple that
we can trust the programmer to get a user-level requirement right if we forget
to specify it.
-
In general, such trust is a bad idea.
- It is better for the specifier to maintain a respectfully and cordially adversarial relationship with the implementor.
-
In many cases, we might consider an application to be sufficiently simple that
we can trust the programmer to get a user-level requirement right if we forget
to specify it.
-
Predicates in Spest use standard Java notation for Boolean expressions,
augmented with additional predicate logic operators.
-
In addition to Java Boolean expressions, we'll use standard Java arithmetic,
and methods available on Java Collections and Strings.
-
These operations are summarized in Table 1.
Predicate Logic: Relational: Operator Description Operator Description && logical and == primitive equality || logical or !- primitive inequality ! logical not < primitive less than if (e1) (e2) logical implication > primitive greater than iff logical equivalence <= primitive less than or equal to if (e1) (e2) else (e3) conditional choice >= primitive grtr than or equal to forall universal quantification .equals object equality exists existential quantification .compareTo object comparison Logical Extensions: Arithmetic: Operator Description Operator Description x' value after execution + addition return return value of method - subtraction * multiplication / division Collections, Lists, Strings: Operator Description .size() size of collection .contains(Object o) collection membership .get(int i) get ith list element .length(String s) length of s other collection ops see Collection docs other list ops see List docs other string ops see String docs Table 1: Spest Expression Operators.
-
The predicate logic operators are used in boolean-valued expressions.
-
Logical and, or, and not have the same meaning as their equivalents in a
programming language, e.g., "&&", "||", and "!" in C and C++.
-
Logical implication and equivalence have their standard logical meanings, per
the following truth tables
p q if (p) q p q p iff q 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
-
The conditional choice operator has the truth table:
p x y p ? x : y 0 x y y 1 x y x
where expressions x and y must have the same type. - The universal and existential quantifiers have their standard logical meanings, but will be applied in specific ways, as upcoming examples illustrate.
-
Logical and, or, and not have the same meaning as their equivalents in a
programming language, e.g., "&&", "||", and "!" in C and C++.
-
The arithmetic operators are used in numeric-valued expressions.
-
Addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication have their standard
mathematical meanings.
-
Remember that preconditions and postconditions are always boolean valued, so
arithmetic must always be performed in the context of a boolean expression.
-
E.g., a + b is not a legal postcondition, but return == a + b
is.
-
Note also that in specifications, we are assuming idealized mathematical
arithmetic, without overflow or underflow
- If the precision of numeric expressions is an issue in a specification, then it must be dealt with explicit logic.
-
Addition, subtraction, division, and multiplication have their standard
mathematical meanings.
-
The collection operators are used with values of java.util.Collection
or java.util.List, the latter used to model collections in which order
must be specified.
-
All other standard Java operators and library methods can be used in predicate
expressions.
-
As always in Java programs, we must be aware of when to use .equals
versus ==.
-
For Spest specifications, == should only be used for primitive types
int, double, and boolean.
-
For all other class-defined types, including String, .equals
is used for testing equality.
- For inequality of class types, use .compareTo.
-
For Spest specifications, == should only be used for primitive types
int, double, and boolean.
-
The predicate logic operators are used in boolean-valued expressions.
-
Further details of the notation are covered in the Java and Spest reference
manuals, available in the
307 doc
directory.
-
The logic of Spest is comparable to other formal specification languages.
-
A difference between our use of Spest and a number of contemporary languages is
collections of instead of mathematical sets.
-
Formally, both collections and sets can be fully axiomatized (i.e.,
mathematically defined), so there is no lack of formality in the use of
collections.
-
In fact, Spest provides definitions of pure Java collections, which
are defined with fully side-effect-free methods.
-
Overall, the use of collections instead of sets results in little difference in
a specification.
-
Set notation makes certain low-level specification easier than with lists, such
as operations that can be modeled with set union and difference.
- On the other hand, collection and list notation makes other forms of specification easier than with sets, such as specification of ordering constraints.
-
Set notation makes certain low-level specification easier than with lists, such
as operations that can be modeled with set union and difference.
-
A difference between our use of Spest and a number of contemporary languages is
collections of instead of mathematical sets.
-
The language of predicates used in pre- and postconditions can be thought of as
non-procedural programming.
-
The rules for this style of "programming" are different than the procedural
kind.
-
We define data, but only in abstract terms and from an end-users "real world"
perspective, not from a computer efficiency perspective.
-
We define functions, but only in abstract terms of what the functions do, not
how they work.
-
Hence, the only "code" we have are boolean expressions at the beginning and
ending of functions, no code bodies.
-
The closest thing we have to traditional control constructs are the two
quantifiers forall and exists.
-
However, these quantifiers are fundamentally different than normal programming
language controls.
- Namely, they only return boolean values, and they don't make anything "happen".
-
However, these quantifiers are fundamentally different than normal programming
language controls.
-
Instead of procedural descriptions of how functions work (i.e., what happens
inside a function), we have only true/false descriptions of what
functions do (i.e., what's true before and after the function
happens).
-
Time does not pass within pre- or postconditions, even ones with quantifiers.
-
Rather, pre- and postconditions are simply statements of mathematical fact,
that are instantaneously true or false.
-
Hence, even though a forall may seem somewhat like a for-loop, it is
just a boolean expression that is only true or false.
- It may be a big boolean expression that is true in a lot of cases, but it's still just a boolean expression.
-
Time does not pass within pre- or postconditions, even ones with quantifiers.
-
We define data, but only in abstract terms and from an end-users "real world"
perspective, not from a computer efficiency perspective.
-
In some cases, it may be necessary to specify certain procedural aspects of a
system, specifically the order in which operations occur.
-
However when we do this we need to be careful not to lapse into conventional
programming.
-
Therefore, we will specify ordering constraints non-procedurally by writing the
precondition of a successor operation to be dependent on the postcondition of a
predecessor operation.
-
E.g., if operation B must follow operation
A, we write the postcondition of A such
that the only way the precondition of B can be true is if
A's postcondition is true.
-
In general, this is accomplished by having A's postcondition
require some unique value for one or more outputs, and then having
B's precondition state that its inputs must have the values
required by A.
- In this way, we require that A must execute before B, if B is ever to happen.
-
E.g., if operation B must follow operation
A, we write the postcondition of A such
that the only way the precondition of B can be true is if
A's postcondition is true.
-
As always, we will specify procedural (i.e., step-by-step) behavior only when
it is fundamental to the way the user operates.
-
In particular, we need to be careful not to specify procedural details of a
particular GUI, when it is only one particular way to access the abstract
operations.
- Here's the way to think about it -- if the user must perform a series of operations in a particular order, then we'll specify the order.
-
However when we do this we need to be careful not to lapse into conventional
programming.
-
For starters with pre- and postconditions, we'll begin with some Calendar tool
operations that are simpler than the scheduling and viewing operations we've
examined in recent weeks.
-
Specifically, we'll look at operations for adding and finding registered
Calendar Tool users and groups.
-
These operations have useful but relatively straightforward specifications.
- Next week we'll return to the specification of the more involved scheduling a viewing operations.
-
When the user selects the 'Users ...' item in the 'Admin'
menu, the system displays the screen shown in Figure 1.
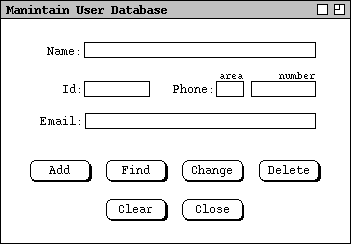
Figure 1: User database maintenance dialog.
-
User Name is a free-form string; Id is a unique system id of
eight characters or less; Email address is free-form string; phone
Area code is three digits, Number is seven digits;
-
The Add command adds a new user; Id field must be unique.
-
The Find command finds by Name or Id or both.
-
If find is by name and the name is not unique, the system displays list of ids
for users of that name.
-
The user clicks on an item in the list to see the full record for that id.
- If no user of the given name or id is found, the system displays a "no users found" pop-up dialog.
-
If find is by name and the name is not unique, the system displays list of ids
for users of that name.
-
Change works after the user changes the most recently displayed
record.
-
Typically, the user runs Find command first, then changes.
- The original record is removed, new record is added.
-
Typically, the user runs Find command first, then changes.
- Delete removes the most recently displayed record, typically located with a Find command; the system displays an "are you sure" pop-up dialog for confirmation.
-
User Name is a free-form string; Id is a unique system id of
eight characters or less; Email address is free-form string; phone
Area code is three digits, Number is seven digits;
-
When the user selects the 'Groups ...' item in the 'Admin'
menu, the system displays the screen in shown Figure 2.
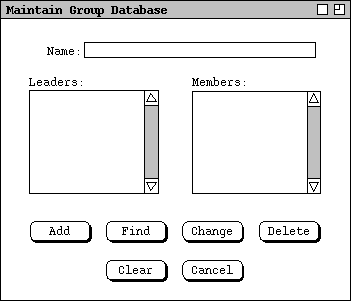
Figure 2: Group database maintenance dialog.
-
Group Name is a free-form string that is unique for all groups;
leaders and Groups are lists of user Ids for the
group leaders and members, respectively; all leaders must be listed as members.
-
The Add command adds a new group; the Name must be unique.
-
The Find command finds a group by name.
-
Change works after the user changes the most recently displayed group
record.
-
Typically, the user runs the Find command first, then changes.
- The original record is removed, the new record is added.
-
Typically, the user runs the Find command first, then changes.
- Delete removes the most recently displayed record, typically located with a Find command; the system displays an "are you sure" pop-up dialog for confirmation.
-
Group Name is a free-form string that is unique for all groups;
leaders and Groups are lists of user Ids for the
group leaders and members, respectively; all leaders must be listed as members.
-
Here are the relevant object and operation definitions:
import java.util.Collection; /** * UserDB is the repository of registered user information. */ abstract class UserDB { /** * The collection of user data records. */ Collection<UserRecord> data; /** * Add the given UserRecord to the given UserDB. The Id of the given user * record must not be the same as a user record already in the UserDB. * The Id component is required and must be eight characters or less. The * email address is required. The phone number is optional; if given, the * area code and number must be 3 and 7 digits respectively. */ abstract void add(UserRecord ur); /** * Find a user by unique id. */ abstract UserRecord findById(String id); /** * Find a user or users by real-world name. If more than one is found, * the output list is sorted by id. */ abstract Collection<UserRecord> findByName(String name); /** * Change the given old UserRecord to the given new record. The old and * new records must not be the same. The old record must already be in * the input db. The new record must meet the same conditions as for the * input to the AddUser operation. Typically the user runs the FindUser * operation prior to Change to locate an existing record to be changed. */ abstract void change(UserRecord old_ur, UserRecord new_ur); /** * Delete the given user record from the given UserDB. The given record * must already be in the input db. Typically the user runs the FindUser * operation prior to Delete to locate an existing record to delete. */ abstract void delete(UserRecord ur); } /** * A UserRecord is the information stored about a registered user of the * Calendar Tool. The Name component is the user`s real-world name. The * Id is the unique identifier by which the user is known to the Calendar * Tool. The EmailAddress is the electronic mail address used by the * Calendar Tool to contact the user when necessary. The PhoneNumber is * for information purposes; it is not used by the Calendar Tool for * contacting the user. */ abstract class UserRecord { String name; String id; String email; PhoneNumber phone; } abstract class PhoneNumber { int area; int number; }
-
For a little practice with UML, Figure 3 shows diagrams for
these definitions, in two equivalent formats.
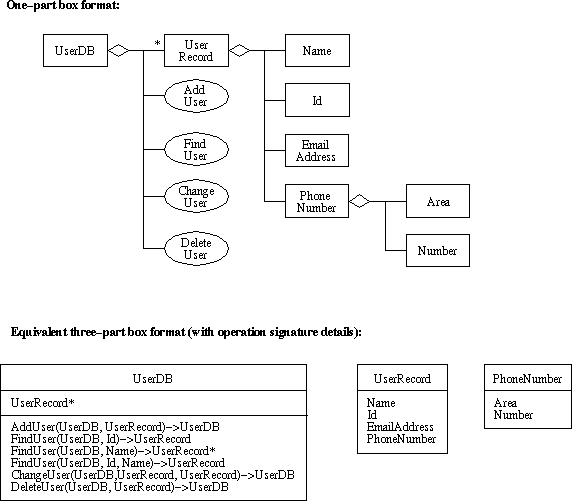
Figure 3: UML diagrams for UserDB objects and operations.
-
The objects and operations were derived from the user-level requirements, per
the model derivation process discussed in
Lecture Notes 5
last week.
-
The operation signatures are quite representative of those defined for a
collection object.
-
UserDB.add is a constructive operation, with a signature of the
general form
class ACollection {
with the effect of adding an element to the data collection.
Collection<AnElement> data;
void constructiveOp(AnElement);
} -
The versions of UserDB.find are selective operations, with signatures
of the general form
class ACollection {
with the effect of finding zero or more elements in a collection.
AnElement selectiveOp(UniqueElementSelector);
Collection<AnElement> selectiveOp(NonUniqueElementSelector);
}-
In both forms, the input is a component of AnElement used as a
search key.
-
In the first form, UniqueElementSelector is a component whose value is
required to be unique among all elements of the collection.
- In the second form, NonUniqueElementSelector is a component whose value is not required to be unique among all elements of the collection.
-
In both forms, the input is a component of AnElement used as a
search key.
-
UserDB.delete is a destructive operation, with the same signature
form as a constructive operation, but with the effect of removing rather than
adding an element.
-
UserDB.change is a modifying operation (combined constructive and
destructive), with a general signature of the form
class ACollection {
with the effect of removing the OldElement and adding the NewElement.
void modifyingOp(AnElement oldElement, AnElement newElement);
}
-
UserDB.add is a constructive operation, with a signature of the
general form
-
In modeling, it can be useful to overload operation names, for better
traceability to the UI.
-
In terms of model accuracy, overloading works well in a case where the same
operational widget (e.g., button) can be used with different input values.
-
Hence, we might overload the find operation thusly:
abstract UserRecord find(String id); abstract Collection<UserRecord> find(String name);
-
The problem is, this form of overloading is not supported in Java, since Java
requires input signatures to differ.
- Hence, where necessary, operations need to be disambiguated by name, as in findById and findByName.
-
In terms of model accuracy, overloading works well in a case where the same
operational widget (e.g., button) can be used with different input values.
-
For operation pre- and postconditions, we will start by stating a predicate in
English, and then refine it into formal logic.
-
As we refine the logic, the English version will be retained as a comment, to
aid in the human understanding of the specification.
-
So, here is an initial version of the formal spec for the UserDB.add
operation:
import java.util.Collection; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /** * Add the given UserRecord ur to this.data. The UserId of the given user * record must not be the same as a user record already in this.data. The * UserId component is required and must be eight characters or less. The * email address is required. The phone number is optional; if given, the * area code and number must be 3 and 7 digits respectively. * <pre> pre: // // The id of the given user record must be unique and less than or // equal to 8 characters; the email address must be non-empty; the // phone area code and number must be 3 and 7 digits, respectively. // post: // // The given user record is in this.data. // * */ abstract void add(UserRecord ur); } -
Now let's formalize the logic.
-
The English comment for the add postcondition specifies the most
fundamental property of an additive collection operation -- upon completion of
the operation, the given element to be added is in the output collection.
-
Formally,
import java.util.Collection; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /** * Add the given UserRecord ur to this.data. The UserId of the given user * record must not be the same as a user record already in this.data. The * UserId component is required and must be eight characters or less. The * email address is required. The phone number is optional; if given, the * area code and number must be 3 and 7 digits respectively. * pre: // // The id of the given user record must be unique and less than or // equal to 8 characters; the email address must be non-empty; the // phone area code and number must be 3 and 7 digits, respectively. // // *** Coming soon *** ; post: // // The given user record is in this.data. // data'.contains(ur); * */ abstract void add(UserRecord ur); }
-
The simple expression "data.contains(ur)'" is all there is to it.
-
contains is a method defined in java.util.Collection.
-
Its operand is a value of the element type contained in the collection.
- I.e., in this case the operand is a UserRecord.
-
contains is a method defined in java.util.Collection.
-
The English comment for the add postcondition specifies the most
fundamental property of an additive collection operation -- upon completion of
the operation, the given element to be added is in the output collection.
-
As it stands, UserDB.add still has no precondition formally defined, only
a comment indicating what needs to be defined.
-
Having no explicit precondition is equivalent to a precondition of true.
-
In many cases, true preconditions are fine, given that there is no specific
condition that must be met before the operation begins.
-
In the case of the UserDB.add operation, a default true precondition definitely
won't do, since we can see from the requirements that a number of conditions
must be met before UserDB.add can proceed.
- We will address these requirements step by step, as we refine the formal definition of UserDB.add.
-
Having no explicit precondition is equivalent to a precondition of true.
-
One of the fundamental questions that must be asked of pre- and postconditions
is if they are strong enough.
-
In general, adding additional predicate
clauses strengthens the conditions.
- For example, the true precondition for UserDB.add is relatively weaker than one that specifies that there is no UserRecord of the same id already in the input database.
-
In general, adding additional predicate
clauses strengthens the conditions.
-
In general, there are two aims to strengthening a specification.
-
Ensuring that all user-level requirements are met (cf. Maxim 1 above).
- Ensuring that a system implementation works properly (cf. Maxim 2).
-
Ensuring that all user-level requirements are met (cf. Maxim 1 above).
-
The former is accomplished via continued consultation with the end user;
the latter requires an experienced analyst, who understands the kinds of
problems that may arise in a system implementation.
-
In the case of the user and group databases, as well as similar database
applications, an area of potential implementation error is the introduction of
spurious entries into the database and/or the spurious deletion of entries.
-
To avoid such spurious effects, the specification of UserDB.add is
strengthened as follows:
import java.util.Collection; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /* post: // // The given user record is in this.data. // data'.contains(ur) && // // All the other records in the output db are those from the input db, // and only those. // forall (UserRecord ur_other ; !ur_other.equals(ur) ; if (data.contains(ur_other)) data'.contains(ur_other) else !data'.contains(ur_other)); */ abstract void add(UserRecord ur); } -
This specification introduces the use of the universal quantification operator,
forall.
-
Universal quantification in Spest has the same meaning as in
standard typed predicate logic.
-
The general format is the following:
forall (T x ; constraint ; predicate)
-
This is read "for all values x of type t, such that
constraint holds, predicate is true."
-
The constraint expression is optional.
- The quantified variable x must appear in constraint (if present) and predicate.
-
This is read "for all values x of type t, such that
constraint holds, predicate is true."
- In general, universal quantification is used frequently when specifying predicates on collection objects, as upcoming examples illustrate.
-
Universal quantification in Spest has the same meaning as in
standard typed predicate logic.
-
While this example is a good illustration of specification strengthening, there
are easier ways to specify the same meaning logically.
-
For example, the postcondition logic can be simplified to the following:
import java.util.Collection; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /* // // A user record is in the output data if and only if it is the new // record to be added or it is in the input data. // post: forall ( UserRecord ur_other ; (data'.contains(ur_other)) iff ur_other.equals(ur) || data.contains(ur_other)); */ abstract void add(UserRecord ur); }
-
In general, predicate simplification is beneficial when it helps clarify the
specification.
- Simplification is not necessary, as long as the logic is clear and accurate.
-
For example, the postcondition logic can be simplified to the following:
-
Another way to simplify this specification is to use a constructive list
operator, as follows:
import java.util.Collection; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /* // // The given user record is in this.data, per the semantics of // Collection.add. // post: data'.equals(data.add(ur)); */ abstract void add(UserRecord ur); }where add in this context is the java.util.Collection.add method.-
A constructive specification such as this describes
the output of an operation using a constructive operation on the inputs.
-
In contrast, an analytic specification (such as the previous spec using
the boolean-valued contains method) describes output without using
constructive operations.
-
In 307, we will define analytic specifications whenever possible.
-
Specifically, we won't used methods that construct or modify collections.
- There is debate among software engineers as to the relative merits of constructive versus non-constructive specification; we will discuss the issues a bit later.
-
Specifically, we won't used methods that construct or modify collections.
-
A constructive specification such as this describes
the output of an operation using a constructive operation on the inputs.
-
Based on the development of the UserDB.add specs so far, we can provide a
comparable level of formal specification for the other three UserDB
operations.
-
For example, here is the idea for formalizing the findById
postcondition:
import java.util.Collection; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /** * Find a user by unique id. * * <pre> post: // // If there is a record with the given id in the input db, then the // output record is equal to that record, otherwise the output record // is empty. * */ UserRecord findById(String id); }
-
Here are the initial formal specifications for the findById,
findByName, ChangeUser, and DeleteUser operations, with the
"no spurious data" requirements.
import java.util.Collection; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /* * Find a user by unique id. * <pre> pre: // None yet. ; post: // // If there is a record with the given id in the input data, then the // output record is equal to that record, otherwise the output record // is null. // exists (UserRecord ur_found ; data.contains(ur_found) ; ur_found.id.equals(id) && ur_found.equals(return)) || !exists ( UserRecord ur_found ; data.contains(ur_found) ; ur_found.id.equals(id)) && return == null; * */ abstract UserRecord findById(String id); /* * Find a user or users by real-world name. If more than one is found, * list is sorted by id. * <pre> pre: // None yet. ; post: // // A record is in the output list if and only it is in the input UserDB // and the record name equals the name being searched for. // forall ( UserRecord ur ; return.contains(ur) iff data.contains(ur) && ur.name.equals(name)); * */ abstract Collection<UserRecord> findByName(String name); /** * Change the given old UserRecord to the given new record. The old and * new records must not be the same. The old record must already be in * the input db. The new record must meet the same conditions as for the * input to the AddUser operation. Typically the user runs the FindUser * operation prior to Change to locate an existing record to be changed. */ /* <pre> pre: // None yet. ; post: // // A user record is in the output data if and only if it is the new // record to be added or it is in the input data, and it is not the old // record. // forall ( UserRecord ur_other ; data'.contains(ur_other) iff ur_other.equals(new_ur) || (data.contains(ur_other) && !ur_other.equals(old_ur))); * */ abstract void change(UserRecord old_ur, UserRecord new_ur); /** * Delete the given user record from the given UserDB. The given record * must already be in the input db. Typically the user runs the FindUser * operation prior to Delete to locate an existing record to delete. * <pre> pre: // None yet. ; post: // // A user record is in the output data if and only if it is not the // existing record to be deleted and it is in the input data. // forall ( UserRecord ur_other ; data'.contains(ur_other) iff !ur_other.equals(ur) && data.contains(ur_other)); * */ abstract void delete(UserRecord ur); } -
Observations.
-
All of the preconditions are commented "None yet."; we will refine
preconditions shortly.
-
The postcondition for findById uses the existential quantifier
exists; details of quantifier formats are coming up.
-
The postcondition for findByName is missing an important piece of logic
vis a vis user-level requirements. What is it? (Hint: see the method's
comment.)
-
The postcondition logic for change and delete are adaptations of
the postcondition logic for add.
-
This kind of logic is sometimes called the "no junk, no confusion" rule for
collection classes.
-
Namely, when we put something into or take something out of a collection,
-
we don't put in or take out anything superfluous (no junk),
- we do put in or take out exactly what we intend to (no confusion).
-
we don't put in or take out anything superfluous (no junk),
- You should study the logic closely to clarify your understanding of it.
-
This kind of logic is sometimes called the "no junk, no confusion" rule for
collection classes.
-
All of the preconditions are commented "None yet."; we will refine
preconditions shortly.
-
Universal and existential quantification are two ways to state multiple
conditions in a single expression.
-
With universal quantification (forall), the quantifier expression is true
if all cases considered are true.
-
With existential quantification (exists), the quantifier expression is
true if at least one of the cases is true.
-
Logically, you can think of forall and exists as forms of repeated
logical and and or, respectively.
-
There is even a generalized DeMorgan's law that makes the two forms of
quantifier interchangeable:
forall (T x ; p) iff !exists (T x ; !p) and !forall (T x ; !p) iff exists (T x ; p)
-
With universal quantification (forall), the quantifier expression is true
if all cases considered are true.
-
In the software modeling task upon which we're focused, the use of logical
quantifiers is focused on two specific objectives:
-
Stating a requirement about all values of a particular type, e.g.,
forall (UserRecord ur ; requirement-predicate)
-
Stating a requirement that must be true for at least one value of a particular
type, e.g.,
exists (UserRecord ur ; requirement-predicate)
-
Stating a requirement about all values of a particular type, e.g.,
-
Constrained forms of qualification provide further focus.
-
Stating a requirement about all values (or at least one value) in a particular
data collection, e.g.,
forall (UserRecord ur ; data.contains(ur) ; requirement-predicate)
exists (UserRecord ur ; data.contains(ur) ; requirement-predicate)
-
Stating a requirement about all values (or at least one value) of a particular
type, with some further restrictions on the values. E.g.,
forall (int i ; i > 0 ; requirement-predicate)
exists (int i ; i > 0 ; requirement-predicate)
-
Stating a requirement about all values (or at least one value) in a particular
data collection, e.g.,
- Keeping these specific focuses in mind will help narrow down when and how to use quantifiers.
-
To this point, we have formalized some basic requirements for our database
operations.
-
Specifically, we have focused on postconditions related to the second of our
formal specification maxims -- not trusting the programmer.
-
It is now time to consider the formal definition of
user-level requirements per the first maxim -- nothing is obvious.
-
To start, there are a number of "obvious" user-level
requirements, including the following:
-
Duplicate entries are not allowed in the UserDB.
-
Input values are checked for validity.
- If the findByName operation outputs more than one record, the output should be sorted in some appropriate order.
-
Duplicate entries are not allowed in the UserDB.
-
We have considered these requirements to some extent in the requirements
narrative.
-
However, the process of fully formalizing the specification can reveal
important details we may have overlooked in the requirements scenarios.
-
For example, in the Milestone 6 scenarios we initially overlooked the sorting
requirement for multiple outputs from findByName.
- Such oversights are common, and one of the main reasons we're doing the fully formal level of the spec.
-
However, the process of fully formalizing the specification can reveal
important details we may have overlooked in the requirements scenarios.
-
An historical note is of interest with regards to such requirements.
-
In software engineering methodologies less formal than what we're using, the
process of formalizing a specification can take the form of "firming up" the
English prose in which the requirements are stated.
-
For example, the first of the
above requirements could be stated "formally" as follows:
A UserDB shall not contain duplicate entries.
-
While this may not seem to be a substantial improvement to the original
statement of the requirement, it represents a seriously-proposed approach to
formalization.
-
With this approach, a number of possible forms of natural language are
standardized with a restricted vocabulary.
- For example, all formal requirements are expressed using "shall" instead of other comparable English words such as "should", "ought to", or "allowed to".
-
With this approach, a number of possible forms of natural language are
standardized with a restricted vocabulary.
-
This idea of formalizing English is noteworthy because it has been widely used
in practice, and significant documents have been "formalized" in this manner.
- While such rules can indeed help with the formalization process, they fall well short of a fully formal basis for requirements specification.
-
In software engineering methodologies less formal than what we're using, the
process of formalizing a specification can take the form of "firming up" the
English prose in which the requirements are stated.
-
Analysis of the no duplicates requirement provides fine support for the
"nothing-is-obvious" maxim.
-
While we may expect reasonable people to understand what "no duplicates" means,
there are in fact a number of plausible interpretations here.
-
Three such
interpretations are the following:
-
No two UserRecords in a UserDB have exactly the same values for all
UserRecord components.
-
No two UserRecords in a UserDB have the same name.
- No two UserRecords in a UserDB have the same id.
-
No two UserRecords in a UserDB have exactly the same values for all
UserRecord components.
-
Which of these interpretations to choose is categorically not a matter
for a programmer to decide.
-
Rather, it should be decided at the user
specification level, by the analyst in consultation with the end users.
-
We could even grant that most programmers are reasonably smart, so in this case
we might safely assume that a programmer could make the correct decision, or
know enough to consult with the user to resolve the ambiguity.
-
Suppose, however, we were specifying data records in a much more complicated
application domain, such as aeronautics.
-
In this domain we might have a data object such as an anomaly list, with record
fields like PreFlight, TaxiOut, InFlight, Approach, and
Landing.
-
What does it mean to disallow duplicates in an anomalies database?
- Which field, if any, could be used as a unique key?
-
What does it mean to disallow duplicates in an anomalies database?
-
The point is that such questions need to be answered by end users and/or
application domain experts.
- Such questions should most certainly not be left unanswered when the programmer begins work, since the programmer may well not know how to answer them, or even that they need to be asked.
-
Rather, it should be decided at the user
specification level, by the analyst in consultation with the end users.
-
In our UserDB case, we have already determined with the customer that the
Id component of a UserRecord is the unique key.
-
This means that UserRecords in the UserDB need
only differ in the Id value.
- In particular, there may be multiple UserRecords with the same name.
-
This means that UserRecords in the UserDB need
only differ in the Id value.
-
The basic strategy for disallowing duplicates is to define a precondition on
UserDB.add that checks for an element of the same Id as the
UserRecord being added.
-
Here is the refined specification for UserDB.add; for brevity, the
postcondition is omitted:
import java.util.Collection; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /** * Same comment as above ... . * <pre> pre: // // There is no user record in the input UserDB with the same id as the // record to be added. // !exists (UserRecord ur_input ; data.contains(ur_input) ; ur_input.id.equals(ur.id)); post: // Same postcondition as above ... ; * */ abstract void add(UserRecord ur); }
-
A discussion of the exact nature of a precondition is in order here.
-
By definition, failure of a precondition means that the operation is prevented
from executing.
-
More precisely, precondition failure means that the operation fails.
-
This abstract meaning of precondition failure does not define how operation
failure is perceived by the end user.
-
Generally, the end-user should see an appropriate error message when an
operation fails.
- The details of such error messages are typically abstracted out of the formal specification.
-
Generally, the end-user should see an appropriate error message when an
operation fails.
-
By definition, failure of a precondition means that the operation is prevented
from executing.
-
Input value constraints for a user record are described in the requirements
scenarios as follows:
-
the Id of a user record is a unique system id of eight characters or less;
-
the email address is a free-form string;
- the phone area code is three digits, the number is seven digits.
-
the Id of a user record is a unique system id of eight characters or less;
-
These constraints are defined formally as follows, with accompanying
commentary:
import java.util.Collection; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /* <pre> pre: // // There is no user record in the input UserDB with the same id as the // record to be added. // !exists (UserRecord ur_other ; data.contains(ur_other) ; ur_other.id.equals(ur.id)) && // // The id of the given user record is not empty and 8 characters or // less. // (ur.id != null) && (ur.id.length() > 0) && (ur.id.length() <= 8) && // // The email address is not empty. // (ur.email != null) && (ur.email.length() > 0) && // // If the phone area code and number are present, they must be 3 digits // and 7 digits respectively. // (if (ur.phone.area != 0) Integer.toString(ur.phone.area).length() == 3) && (if (ur.phone.number != 0) Integer.toString(ur.phone.number).length() == 7); post: // Same as above ; * */ abstract void add(UserRecord ur); }
-
Observations
-
The standard way to strengthen a precondition is to and on additional
clauses.
-
Here, the previous "no duplicates" clause remains.
- The new requirements are added by anding them on.
-
Here, the previous "no duplicates" clause remains.
-
The process of formally specifying these requirements led to the discovery of
one unnoticed requirements detail, which will be updated in the scenario
narrative.
-
Specifically, in considering the formal specification for the constraint on
email address, we were alerted to the question of whether it should be
required.
-
In consultation with the customer, the answer turns out to be "yes", even
though we had not originally considered the issue explicitly in the scenarios.
-
Hence, there is the precondition clause
(ur.email != null) && (ur.email.length() > 0)
-
This says that while the email address can be a free-form string, it cannot be
null or of length 0, i.e., the user cannot leave it empty in the dialog.
-
Note that we include a standard Java practice of checking for a null reference
value before accessing a component of that reference.
- Predicates should not throw exceptions, unless they are explicitly dealt with in the specification, which subject we will address next week.
-
Note that we include a standard Java practice of checking for a null reference
value before accessing a component of that reference.
- Such are just the kind of details we hope to catch while formalizing.
-
In consultation with the customer, the answer turns out to be "yes", even
though we had not originally considered the issue explicitly in the scenarios.
-
The standard way to strengthen a precondition is to and on additional
clauses.
-
The version of findByName input produces a list of UserRecords,
since the name input is not required to be a unique-valued component of a
record.
-
As noted above, the initial requirements scenario overlooked what order the
outputs should be in, if there are two or more.
-
The most reasonable choice is to sort the output list by Id field.
-
The scenario narrative will be updated to reflect this decision.
-
As with other such requirements, we should not trust that a programmer will do
the right thing in the absence of a formal statement.
-
In this case, the programmer may not even think there is problem if an output
list is displayed in some internal order, such as the order UserRecords
are stored in a hash table.
- Such an order is as good as random to most human users, and as such rarely if ever satisfactory.
-
The scenario narrative will be updated to reflect this decision.
-
To specify UserRecord list ordering, we must strengthen the
findByName postcondition. Here it is:
import java.util.Collection; import java.util.List; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /** * Find a user or users by real-world name. If more than one is found, * the output list is sorted by id. * <pre> pre: // Not defined yet. ; post: // // The output list consists of all records of the given name in the // input data. // forall (UserRecord ur ; return.contains(ur) ; data.contains(ur) && ur.name.equals(name)) && // // The output list is sorted lexicographically by id, according to the // semantics of java.lang.String.compareTo(). // forall (int i ; (i >= 0) && (i < return.size() - 1) ; return.get(i).id.compareTo(return.get(i+1).id) < 0); * */ abstract List<UserRecord> findByName(String name); }
-
An English translation of the sorting logic is the following:
"For each position i in the output list, such that i is between the first and the second to the last positions in the list, the ith element of the list is less than the i+1st element of the list."
-
You should study this logic to be satisfied that it specifies sorting
satisfactorily.
-
Note that we have used the java.util.List interface to define our
collection object.
-
We'll use List instead of Collection in a specification when we need
to specify ordering
- java.util.Collection does not have the get method for selecting the ith element.
-
We'll use List instead of Collection in a specification when we need
to specify ordering
-
What would happen to the meaning of the sorting predicate if the constraint
on the range of i were not present?
-
I.e., if the sorting logic in the postcondition were changed to the following:
forall (int i ; return.get(i).id.compareTo(return.get(i+1).id) < 0)
-
The meaning here is an unbounded quantification.
-
That is, the quantifier operates over the unbounded range of all integers.
-
In pure mathematical terms, unbounded means infinite.
- In terms of a Java program, numbers are bounded by the word size of a particular computer architecture, but we are abstracting that out of our specifications at the moment.
-
In pure mathematical terms, unbounded means infinite.
-
In principle, there is nothing wrong with unbounded quantification.
-
For example, the original anti-spurious requirements for UserDB.add are
expressed using unbounded quantification
-
I.e., forall (UserRecord ur ...)
- The range of the UserRecord type is unbounded, since it constrains string components, the values of which are conceptually unbounded, due to their conceptually unbounded length.
-
I.e., forall (UserRecord ur ...)
- One might argue for range restrictions on the grounds of efficiency, but as noted earlier, efficiency of this nature is not of concern in an abstract specification.
-
That is, the quantifier operates over the unbounded range of all integers.
-
The potential problem with unbounded quantification is that the body of the
universal quantifier may not have the correct value in an unbounded range, and
hence the value of the entire quantifier expression may be false when we expect
it to be true, or may throw an exception, which we do not want.
-
This is in fact the case in the unbounded quantification used in the sorting
predicate for findByName.
- Specifically, the evaluation of return.get(i) throws an exception if i is outside the bounds of return.
-
This is in fact the case in the unbounded quantification used in the sorting
predicate for findByName.
-
The exact outcome of the unbounded quantification depends on the semantics,
i.e., formal definition, of a particular specification language.
-
In general, however, unbounded quantification is potentially problematic under
any logical semantics.
-
The point is that one needs to be careful when using unbounded quantification
to ensure that the body of the quantifier has a well understood value over the
entire unbounded range of quantification.
- This is particularly the case when quantifying over the elements of a list.
-
In general, however, unbounded quantification is potentially problematic under
any logical semantics.
-
The postcondition in the most recent definition of findByName is a little
lengthy.
-
In practice, predicates significantly longer than this can appear in
the specification of a complex operation.
-
When pre- or postconditions become unduly long, it is useful to use
auxiliary functions to organize the logic.
-
In Spest, an auxiliary function is defined as a boolean-valued method in the
class where the function is used in a predicate.
-
The logic of the auxiliary function is defined with a postcondition of the
form "return == ...", where "..." is a boolean expression that
appears in one or more predicates.
-
The purpose of an auxiliary function is simply to modularize a piece of logic,
give it a mnemonic name, and allow that logic to be invoked in one or more
places.
- I.e., the purpose is to make predicates more readable and understandable.
-
In practice, predicates significantly longer than this can appear in
the specification of a complex operation.
-
As an example, here is the preceding definition of findByName using two
auxiliary functions.
import java.util.Collection; import java.util.List; abstract class UserDB { Collection<UserRecord> data; /** * Find a user or users by real-world name. If more than one is found, * the output list is sorted by id. * <pre> pre: // Not defined yet. ; post: recordsFound(name, return) && sortedById(return); * */ abstract List<UserRecord> findByName(String name); /** * Return true if the given list consists of all records of the given name * in this.data. * <pre> post: return == forall (UserRecord ur ; list.contains(ur) iff data.contains(ur) && ur.name.equals(name)); * */ abstract boolean recordsFound(String name, Collection<UserRecord> list); /** * Return true if the given list is sorted lexicographically by id, * according to the semantics of java.lang.String.compareTo(). * <pre> post: return == forall (int i ; (i >= 0) && (i < list.size() - 1) ; list.get(i).id.compareTo(list.get(i+1).id) < 0); * */ abstract boolean sortedById(List<UserRecord> list); }
-
Figure 2 on page 2 shows the UI for the other user-related database
in the Calendar Tool -- the database of user groups.
-
The specs for the GroupDB are quite similar to UserDB.
-
Both databases are clear examples of collection objects with typical collection
operations.
- The specs for GroupDB are slightly simpler, given that there is only one searchable component, the group name, which must be unique among all groups in the database.
-
Both databases are clear examples of collection objects with typical collection
operations.
-
A significant specification issue does arise in the area of interaction between
user database operations with the group database.
-
Specifically, what happens to groups that have as a member a user who is
deleted from the user database?
-
Possible ways to deal with this problem include the following:
-
A deleted user is automatically removed from all groups of which she is a
member.
-
If a deleted user is in one or more groups, a warning message is output
indicating what groups the user was in, but the users must be manually deleted
from the groups; in the meantime, any unknown users are simply ignored in the
group member lists.
- The system prevents deletion of a user until she has first been deleted from all groups; to assist the deletion, the system outputs a message indicating the affected groups.
-
A deleted user is automatically removed from all groups of which she is a
member.
-
Specifically, what happens to groups that have as a member a user who is
deleted from the user database?
-
This is yet another example of where formalizing the specs has led to the
discovery of an important requirements issue.
-
In this case, user consultation results in the automatic removal solution.
-
This in turn leads to another issue, which is what should be done with groups
who have no leader, due to the automatic deletion of a member or was the only
leader of a group.
- This issue is resolved by allowing leaderless groups, but having the system output a warning when the situation arises.
-
In this case, user consultation results in the automatic removal solution.
-
All of the issues having been resolved, the resulting complete spec for the
user and group databases is as follows:
/* * * This file defines the objects and operations related to maintaining the * user, group, and location databases of the calendar system. See Section 2.6 * of the Milestone 8 requirements. */ import java.util.Collection; import java.util.List; /** * UserDB is the repository of registered user information. */ abstract class UserDB { /** * The collection of user data records. */ Collection<UserRecord> data; /** * Reference to GroupDB needed for change and delete methods. */ GroupDB groupDB; /** * Add the given UserRecord to the given UserDB. The Id of the given user * record must not be the same as a user record already in the UserDB. * The Id component is required and must be eight characters or less. The * email address is required. The phone number is optional; if given, the * area code and number must be 3 and 7 digits respectively. * <pre> pre: // // There is no user record in the input UserDB with the same id as the // record to be added. // !exists (UserRecord ur_other ; data.contains(ur_other) ; ur_other.id.equals(ur.id)) && // // The id of the given user record is not empty and 8 characters or // less. // (ur.id != null) && (ur.id.length() > 0) && (ur.id.length() <= 8) && // // The email address is not empty. // (ur.email != null) && (ur.email.length() > 0) && // // If the phone area code and number are present, they must be 3 digits // and 7 digits respectively. // if (ur.phone.area != 0) ( Integer.toString(ur.phone.area).length() == 3) && if (ur.phone.number != 0) ( Integer.toString(ur.phone.number).length() == 7); post: // // A user record is in the output data if and only if it is the new // record to be added or it is in the input data. // forall (UserRecord ur_other ; (data'.contains(ur_other)) iff ur_other.equals(ur) || data.contains(ur_other)); * */ abstract void add(UserRecord ur); /** * Find a user by unique id. * <pre> post: // // If there is a record with the given id in the input data, then the // output record is equal to that record, otherwise the output record // is null. // exists (UserRecord ur_found ; data.contains(ur_found) ; ur_found.id.equals(id) && ur_found.equals(return)) || !exists (UserRecord ur_found ; data.contains(ur_found) ; ur_found.id.equals(id)) && return == null; * */ abstract UserRecord findById(String id); /** * Find a user or users by real-world name. If more than one is found, * then the output list is sorted by id. * <pre> post: // // The output list consists of all records of the given name in the // input data. // forall (UserRecord ur ; return.contains(ur) ; data.contains(ur) && ur.name.equals(name)) && // // The output list is sorted lexicographically by id, according to the // string comparison semantics of java.lang.String.compareTo(). // forall (int i ; (i >= 0) && (i < return.size() - 1) ; return.get(i).id.compareTo(return.get(i+1).id) < 0); * */ abstract List<UserRecord> findByName(String name); /** * Change the given old UserRecord to the given new record. The old and * new records must not be the same. The old record must already be in * the input db. The new record must meet the same conditions as for the * input to the AddUser operation. Typically the user runs the FindUser * operation prior to Change to locate an existing record to be changed. * * If the user record id is changed, then change all occurrences of the * old id in the group db to the new id. * <pre> pre: // // The old and new user records are not the same. // !old_ur.equals(new_ur) && // // The old record is in this.data. // data.contains(old_ur) && // // There is no user record in the input UserDB with the same id as the // new record to be added. // ! exists (UserRecord ur_other ; data.contains(ur_other) ; ur_other.id.equals(new_ur.id)) && // // The id of the new record is not empty and 8 characters or less. // (new_ur.id != null) && (new_ur.id.length() > 0) && (new_ur.id.length() <= 8) && // // The email address is not empty. // (new_ur.email != null) && (new_ur.email.length() > 0) && // // If the phone area code and number are present, they must be 3 digits // and 7 digits respectively. // if (new_ur.phone.area != 0) ( Integer.toString(new_ur.phone.area).length() == 3) && if (new_ur.phone.number != 0) ( Integer.toString(new_ur.phone.number).length() == 7); post: // // A user record is in the output data if and only if it is the new // record to be added or it is in the input data, and it is not the old // record. // forall (UserRecord ur_other ; data'.contains(ur_other) iff ur_other.equals(new_ur) || (data.contains(ur_other) && !ur_other.equals(old_ur))) && // // If new id is different than old id, then all occurrences of old id // in the GroupDB are replaced by new id. // if (!old_ur.id.equals(new_ur.id) (true) // Logic left as exercise for the reader ; * */ abstract void change( UserRecord old_ur, UserRecord new_ur); /** * Delete the given user record from the given UserDB. The given record * must already be in the input db. Typically the user runs the FindUser * operation prior to Delete to locate an existing record to delete. * * In addition, delete the user from all groups of which the user is a * member. If the deleted user is the only leader of a one more groups, * output a warning indicating that those groups have become leaderless. * <pre> pre: // // The given user record is in this.data. // data.contains(ur); post: // // A user record is in the output data if and only if it is not the // existing record to be deleted and it is in the input data. // forall (UserRecord ur_other ; data'.contains(ur_other) iff !ur_other.equals(ur) && data.contains(ur_other)) && // // The id of the deleted user is not in the leader or member lists of // any group in the output GroupDB. (NOTE: This clause is not as // strong as a complete "no junk, no confusion" spec. Why not? Should // it be?) // forall (GroupRecord gr ; groupDB.data.contains(gr) ; !gr.leaders.contains(ur.id) && !gr.members.contains(ur.id)) && // // The LeaderlessGroupsWarning list contains the ids of all groups // whose only leader was the user who has just been deleted. // forall (GroupRecord gr ; groupDB.data.contains(gr) ; forall (String id ; (return.groupNames.contains(id) iff gr.leaders.size() == 1) && (gr.leaders.get(0).equals(ur.id)))); * */ abstract LeaderlessGroupsWarning delete(UserRecord ur); } /** * A UserRecord is the information stored about a registered user of the * Calendar Tool. The Name component is the user`s real-world name. The * Id is the unique identifier by which the user is known to the Calendar * Tool. The EmailAddress is the electronic mail address used by the * Calendar Tool to contact the user when necessary. The PhoneNumber is * for information purposes; it is not used by the Calendar Tool for * contacting the user. */ abstract class UserRecord { String name; String id; String email; PhoneNumber phone; } abstract class PhoneNumber { int area; int number; } /** * LeaderlessGroupsWarning is a secondary output of the UserDB.change and * UserDB.delete operations, indicating the names of zero or more groups that * have become leaderless as the result of a user having been deleted. */ abstract class LeaderlessGroupsWarning { Collection<String> groupNames; } /** * GroupDB is the repository of user group information. */ abstract class GroupDB { /** * The collection of group data records. */ Collection<GroupRecord> data; /** * Reference to GroupDB needed for change and delete methods. */ UserDB userDB; /** * Add the given GroupRecord to the given GroupDB. The name of the given * group must not be the same as a group already in the GroupDB. All * group members must be registered users. The leader(s) of the group * must be members of it. * <pre> pre: // // All group members are registered users. // forall (String id ; gr.members.contains(id) ; exists (UserRecord ur ; userDB.data.contains(ur) ; ur.id.equals(id))) && // // All group leaders are members of the group. // forall (String id ; gr.leaders.contains(id) ; gr.members.contains(id)); post: // // A group record is in the output db if and only if it is the new // record to be added or it is in the input db. // forall (GroupRecord gr_other ; data'.contains(gr_other) iff gr_other.equals(gr) || data.contains(gr_other)); * */ abstract void add(GroupRecord gr); /** * Delete the given group record from the given GroupDB. The given record * must already be in the input db. Typically the user runs the FindGroup * operation prior to Delete to locate an existing record to delete. * <pre> pre: // // The given GroupRecord is in the given GroupDB. // data.contains(gr); post: // // A group record is in the output db if and only if it is not the // existing record to be deleted and it is in the input db. // forall (GroupRecord gr_other ; data'.contains(gr_other) iff !gr_other.equals(gr) && data.contains(gr_other)); * */ abstract void delete(GroupRecord gr); /** * Change the given old GroupRecord to the given new record. The old and * new records must not be the same. The old record must already be in * the input db. The new record must meet the same conditions as for the * input to the AddGroup operation. Typically the user runs the FindGroup * operation prior to Change to locate an existing record to be changed. * <pre> pre: // // The old and new group records are not the same. // !old_gr.equals(new_gr) && // // All group members are registered users. // forall (String id ; new_gr.members.contains(id) ; exists (UserRecord ur ; userDB.data.contains(ur) && ur.id.equals(id))) && // // All group leaders are members of the group. // forall ( String id ; new_gr.leaders.contains(id) ; new_gr.members.contains(id)); post: // // A group record is in the output db if and only if it is the new // record to be added or it is in the input db, and it is not the old // record. // forall (GroupRecord gr_other ; data'.contains(gr_other) iff gr_other.equals(new_gr) || data.contains(gr_other) && !gr_other.equals(old_gr)); * */ abstract void change(GroupRecord old_gr, GroupRecord new_gr); /** * Find a group by unique name. * <pre> post: // // If there is a record with the given name in the input db, then the // output record is equal to that record, otherwise the output record // is empty. // exists (GroupRecord gr_found ; data.contains(gr_found) ; gr_found.name.equals(id) && gr_found.equals(return)) || !exists (GroupRecord gr_found ; data.contains(gr_found) ; gr_found.name.equals(id) && return == null); * */ abstract GroupRecord findById(String id); } /** * A GroupRecord is the information stored about a user group. The Name * component is a unique group name of any length. Leaders is a list of zero * or more users designated as group leader. Members is the list of group * members, including the leaders. Both lists consist of user id's. Normally * a group is required to have at least one leader. The only case that a * group becomes leaderless is when its only leader is deleted as a registered * user. */ abstract class GroupRecord { String name; List<String> leaders; List<String> members; } /** * The LocationDB contains the location records that provide information about * the locations at which items are scheduled. */ abstract class LocationDB { Collection<LocationRecord> data; } /** * A LocationRecord has a name and number which serve to identify where * the location is. Both fields are free-form strings and the Calendar * Tool enforces no constraints on their values. The Bookings component * is a list of the titles of the items that are scheduled in the * location. The Remarks component is a free-form text that can be used * to describe any other pertinent information about the room. */ abstract class LocationRecord { String name; String number; Bookings bookings; Remarks remarks; } abstract class Bookings { /* ... */ } abstract class Remarks { /* ... */ }