-
As discussed in Lecture Notes 3, model classes that trace to objects in the
abstract specification inherit from the Model abstract class.
-
Similarly, view classes that trace to elements of the concrete end-user
interface inherit from the View abstract class.
-
The Java definitions of the Model and View classes follow.
-
The comments in those classes provide details and rationale for the class
designs.
-
The method comments have preconditions and postconditions, details of which are
in week 5 notes.
-
As noted in Week 3 lecture discussions, you are most welcome to, but not
required to use mvp classes in your 309 design.
-
The code itself is in 309/lib/source/java/mvp.
- The linkable jar file is in 309/lib/csc309libs.jar
-
The comments in those classes provide details and rationale for the class
designs.
-
mvp.Model
package mvp; import java.util.*; import java.io.*; /**** * * Class Model is an abstract parent class for model classes in an MVP design. * See <a href = "http://www.csc.calpoly.edu/~gfisher/classes/309/lectures"> * Fisher SE lecture notes </a> for further discussion of the MVP design * methodology. * * @author Gene Fisher (gfisher@calpoly.edu) * @version cvs 1.12, 2005/02/02 * */ public abstract class Model extends Observable implements Serializable { /** * Construct a model with the given View. * <pre> * post: this'.view = view; * </pre> */ public Model(View view) { this.view = view; } /** * Construct a model with no view. This constructor is typically used for * submodel objects that have no individual view of their own, but have a * subview that is part of a larger parent's view. * <pre> * post: this'.view = null; * </pre> */ public Model() { view = null; } /** * Set the view of this to the given view, if the view is not already set. * This setView method is used if this must be constructed before its * companion view is constructed, and therefore the view will not be * available to pass to the constructor. * <p> * Models with multiple and/or dynamically changeable views must manage * view changes with additional data members. This' canonical view can be * set only once, with either the constructor or one call to setView. * <pre> * pre: this.view == null; * * post: this'.view == view; * </pre> */ public void setView(View v) { if (this.view == null) this.view = v; } /** * Return the view of this. * <pre> * post: return == view; * </pre> */ public View getView() { return view; } /** * Perform appropriate exit processing, which typically includes exiting * the application program of which this model is a component. This method * is called from a companion view when the view's window is closed, and * such closing means that the application should exit. See <a href= * View.html#setExitOnClose(boolean)> <tt>View.setExitOnClose</tt> </a> for * more information. * <pre> * post: ; // must be specialized in subclasses * </pre> */ public void exit() {} /** * Dump the entire contents of this in String form. This method is * intended to be called during testing to produce an inspectable and * difference version of this model's data. This dump method is distinct * from the Object.toString method in Java, since toString may be used for * other purposes than producing a complete data dump. * <pre> * post: ; // must be specialized in subclasses * </pre> */ public String dump() { return null; } /** The canonical view for this model. Models with multiple views can add * additional view data members as necessary. */ protected View view; }
-
mvp.View
package mvp; import java.awt.*; import java.awt.event.*; import java.util.*; import java.io.*; /**** * * Class View is an abstract parent class for view classes in an MVP design. * See <a href = "http://www.csc.calpoly.edu/~gfisher/classes/309/lectures"> * Fisher SE lecture notes </a> for further discussion of the MVP design * methodology. * <p> * View implements Observer since it is often convenient for a view to observe * its companion model, particularly when a model has multiple views that all * need to change simultaneously when the model changes. View implements * Serializable as a convenience for serializing models that refer to views. * Typically, view data are not themselves worthy of serialization, but when a * model refers to a view, that view needs to be Serializable in principle in * order for serialization to proceed without problems. * * @author Gene Fisher (gfisher@calpoly.edu) * @version cvs 1.15, 2005/02/02 * */ public abstract class View implements Observer, Serializable { /** * Construct a view with the given Screen and Model. Initialize other data * members to null or false, as appropriate. The given screen is that in * which the view will insert itself to be physically displayed. The model * is the companion model in an MVP design. * <pre> * pre: screen != null; * * post: (this'.screen == screen) && (this'.model == model) && * (window' == null) && (shown' == false) && * (editable' == false) && (closeAdapter == false); * </pre> */ public View(Screen screen, Model model) { this.screen = screen; this.model = model; shown = false; editable = false; } /** * Construct this with a null screen and model. Initialize other data * members to null or false, as appropriate. * <pre> * post: (this'.screen == null) && (this'.model == null) && * (window' == null) && (shown' == false) && * (editable' == false) && (closeAdapter == false); * </pre> */ public View() { shown = false; editable = false; } /** * Run this by entering the screen's event loop, which will in turn display * the window of this and any widgets within the window. In a * non-modal GUI, only the topmost view will be run. In a modal GUI, run * is specialized in View subclasses to contain a modal event loop that * locks out events from other view components until the event loop has * been completed, e.g., by the user selecting 'OK' or 'Cancel'. * <pre> * pre: ! screen.isRunning(); * * post: screen'.isRunning() && * forall (Component c | c in screen.getComponents()) * c.isDisplayed(); * </pre> * where <tt>isRunning</tt> is an assumed predicate of <tt>Screen</tt> that * returns true if the Screen's event-handling loop is running. */ public void run() { // A noop in Java } /** * Compose the interface components of this, setting the window and/or * widget fields to the top-level of the composition. Note that compose * does not physically display this, it only constructs its components so * it may subsequently be displayed with the run and show methods. As a * convenience to callers, compose returns the widget field of this, since * it is frequently accessed after composition. * <pre> * post: return == widget; // Compose must be specialized in subclasses. * </pre> */ public Component compose() { return widget; } /** * Insert the window of this into the screen, thereby physically displaying * it. Upon insertion, the window will be the frontmost of all other * screen windows. If this is already displayed, Show has the effect of * moving its window to the front of all other windows. * <p> * To move the window to some position other than the front, extract the * window with this.getWindow and manipulate it with methods available in * the Window class. * <p> * The screen position of the window will be selected by the underlying * window manager. To show the window of this at a specific screen * position, use the overloaded version of Show specified below. * <pre> * pre: ; * * post: if (window != null) * then screen'.isDisplayed(window) && * screen'.IsFrontmost(window) && * shown' == true; * else System.out.println("error"); * </pre> */ public void show() { if (window == null) { System.out.print("The window data member of this view:\n "); System.out.print(this.getClass().getName()); System.out.println("\nis null."); } else { window.setVisible(true); shown = true; } } /** * Same specs as Show(), except the window is shown at the given x,y * coordinate. The x,y coordinate system is in units of screen pixels, * with the 0,0 origin in the lower left corner of the screen. The given * x,y coordinates refer to the lower left corder of the window. */ public void show(int x, int y) { window.setLocation(new Point(x, y)); show(); } /** * Remove the window of this from the screen, thereby physically * undisplaying it. * <pre> * pre: ; // Note that the window may or may not be currently displayed * * post: ! screen'.isDisplayed(window) && * (shown' == false); * </pre> */ public void hide() { window.setVisible(false); shown = false; } /** * Update the displayed data in this. The processing involved in this * update is strictly view specific. Generally, the view will call one or * more methods in the companion model to obtain the necessary data to * perform the update. * <p> * Views that do not change in response to changes in model data typically * do not implement update. For example, a dialog that is used strictly * for user input does not need to implement update. In contrast, a view * that displays changing model data does indeed need to implement update. * <pre> * post: ; // Update must be specialized in subclasses. * </pre> */ public void update(Observable o, Object arg) {} /** * Return the model of this. * * post: return == model; */ public Model getModel() { return model; } /** * Set the model of this to the given model, if the model is not already * set. This setModel method is used if this must be constructed before * its companion model is constructed, and therefore the model will not be * available to pass to the constructor. * <pre> * pre: this.model == null; * * post: this.model' == model; * </pre> */ public void setModel(Model model) { if (this.model == null); this.model = model; } /** * Return the window of this. * <pre> * post: return == window; * </pre> */ public Window getWindow() { return window; } /** * Return the widget of this. * <pre> * post: return == widget; * </pre> */ public Component getWidget() { return widget; } /** * Return true if this is currently displayed on the screen. * <pre> * post: return == shown; * </pre> */ public boolean isShown() { return shown; } /** * Return true if this is currently editable. The editability of a view * dictates whether the user is allowed to enter values in the view's * components that are normally editable, e.g., string or text editors. * <pre> * post: return == editable; * </pre> */ public boolean isEditable() { return editable; } /** * Set the editability of this to the given boolean value. * <pre> * post: this'.editable == editable; * </pre> */ public void setEditable(boolean editable) { this.editable = editable; } /** * Perform the necessary set up to call or not to call the companion * model's <tt>exit</tt> method when the user closes this' window. When * <tt>exitOnClose</tt> is true, <tt>model.exit</tt> is called upon window * close; when <tt>exitOnClose</tt> is false, <tt>model.exit</tt> is not * called. From the user's perspective, the close is performed using a * command provided by the underlying window manager, e.g., a window close * button. * <pre> * pre: (window != null) * * post: if (exitOnClose == true) * then (exists (WindowAdapter wa) * (wa in window.getListeners(WindowAdapter.class)) && * (wa.getClass().getDeclaredMethod( * "windowClosing", {WindowEvent.class})).invokes( * model.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("exit", null)) && * (closeAdapter' == wa)) * else !(exists (WindowAdapter wa) * (wa in window.getListeners(WindowAdapter.class)) && * (wa.getClass().getDeclaredMethod( * "windowClosing", {WindowEvent.class})).invokes( * model.getClass().getDeclaredMethod("exit", null))) && * (closeAdapter' == null) * </pre> */ public void setExitOnClose(boolean exitOnClose) { /* * Outta here if window is null. */ if (window == null) return; /* * If the exitOnClose input argument is true, add a listen-for-close * window adapter to this' window, if one hasn't already been added. * If false, remove the listener if it's there. */ if (exitOnClose && (closeAdapter == null)) { window.addWindowListener(closeAdapter = new WindowAdapter() { public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { model.exit(); } }); } if (!exitOnClose && (closeAdapter != null)) { window.removeWindowListener(closeAdapter); closeAdapter = null; } } /** The unique companion model for this */ protected Model model; /** The physical display screen for this. Only views that have a non-null * Window (see below) need a value for the Screen. Otherwise, the value of * the Screen member is null. */ protected Screen screen; /** The physical UI window for this. The Window is the stand-alone * top-level window for the view, displayed on the screen by the underlying * window manager. For views that do not have a managed window, e.g., * pulldown menu or dialog contained in another view, the Window member is * null. */ protected Window window; /** The outermost interactive element (i.e., "widget") for this. In some * toolkits, Window and Widget are the same type. In such cases, if a view * has an non-null Window, then it does not need a value for Widget. In * toolkits such as Java Swing, where Window and Widget are distinct types, * a view may need both a value for the Window and Widget. */ protected Component widget; /** True if the window is displayed */ protected boolean shown; /** True if this is editable */ protected boolean editable; /** The exit-on-close listener */ protected WindowAdapter closeAdapter; }
-
To illustrate how methods are invoked in an event-based design, there are a
number of method backtraces shown below.
-
A backtrace shows the order in which methods are called when a particular
action is performed.
- The backtraces shown below were generated using the jdb debugger; similar backtraces are produced by IDEs, such as NetBeans and Eclipse.
-
A backtrace shows the order in which methods are called when a particular
action is performed.
-
The following backtrace illustrates set up of the File menu, in
particular how the method that adds the New item to the File menu
is called.
[1] caltool.file_ui.FileMenu.addNewItem (FileMenu.java:111) [2] caltool.file_ui.FileMenu.compose (FileMenu.java:64) [3] caltool.file_ui.FileUI.compose (FileUI.java:35) [4] caltool.caltool_ui.CalendarToolUI.composeMenuBar (CalendarToolUI.java:186) [5] caltool.caltool_ui.CalendarToolUI.compose (CalendarToolUI.java:114) [6] caltool.CalendarTool.main (CalendarTool.java:114)
-
The following backtraces illustrates set up of an event listener, in particular
the listener associated with the OK button in the
SCheduleEventDialog.
[1] caltool.schedule_ui.OKScheduleEventButtonListener.<init> (OKScheduleEventButtonListener.java:32) [2] caltool.schedule_ui.ScheduleEventDialog.composeButtonRow (ScheduleEventDialog.java:251) [3] caltool.schedule_ui.ScheduleEventDialog.compose (ScheduleEventDialog.java:96) [4] caltool.schedule_ui.ScheduleUI.compose (ScheduleUI.java:56) [5] caltool.caltool_ui.CalendarToolUI.composeMenuBar (CalendarToolUI.java:188) [6] caltool.caltool_ui.CalendarToolUI.compose (CalendarToolUI.java:114) [7] caltool.CalendarTool.main (CalendarTool.java:114)
-
The following backtrace illustrates the event-based invocation of a method
associated with a menu item, specifically the File.fileNew method.
[1] caltool.file.File.fileNew (File.java:36) [2] caltool.file_ui.FileMenu$1.actionPerformed (FileMenu.java:117) [3] javax.swing.AbstractButton.fireActionPerformed (AbstractButton.java:1,819) [4] javax.swing.AbstractButton$ForwardActionEvents.actionPerformed (AbstractButton.java:1,872) [5] javax.swing.DefaultButtonModel.fireActionPerformed (DefaultButtonModel.java:420) [6] javax.swing.DefaultButtonModel.setPressed (DefaultButtonModel.java:258) [7] javax.swing.AbstractButton.doClick (AbstractButton.java:321) [8] javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicMenuItemUI.doClick (BasicMenuItemUI.java:1,113) [9] javax.swing.plaf.basic.BasicMenuItemUI$MouseInputHandler.mouseReleased (BasicMenuItemUI.java:943) [10] java.awt.Component.processMouseEvent (Component.java:5,166) [11] java.awt.Component.processEvent (Component.java:4,963) [12] java.awt.Container.processEvent (Container.java:1,613) [13] java.awt.Component.dispatchEventImpl (Component.java:3,681) [14] java.awt.Container.dispatchEventImpl (Container.java:1,671) [15] java.awt.Component.dispatchEvent (Component.java:3,543) [16] java.awt.LightweightDispatcher.retargetMouseEvent (Container.java:3,527) [17] java.awt.LightweightDispatcher.processMouseEvent (Container.java:3,242) [18] java.awt.LightweightDispatcher.dispatchEvent (Container.java:3,172) [19] java.awt.Container.dispatchEventImpl (Container.java:1,657) [20] java.awt.Window.dispatchEventImpl (Window.java:1,606) [21] java.awt.Component.dispatchEvent (Component.java:3,543) [22] java.awt.EventQueue.dispatchEvent (EventQueue.java:456) [23] java.awt.EventDispatchThread.pumpOneEventForHierarchy (EventDispatchThread.java:234) [24] java.awt.EventDispatchThread.pumpEventsForHierarchy (EventDispatchThread.java:184) [25] java.awt.EventDispatchThread.pumpEvents (EventDispatchThread.java:178) [26] java.awt.EventDispatchThread.pumpEvents (EventDispatchThread.java:170) [27] java.awt.EventDispatchThread.run (EventDispatchThread.java:100)
-
The following backtrace illustrates the event-based invocation of a method
associated with a dialog button, in particular the Schedule.scheduleEvent
method invoked from the OK button in the ScheduleEventDialog.
[1] caltool.schedule.Schedule.scheduleEvent (Schedule.java:93) [2] caltool.schedule_ui.OKScheduleEventButtonListener.actionPerformed (OKScheduleEventButtonListener.java:50) [3] javax.swing.AbstractButton.fireActionPerformed (AbstractButton.java:1,819)
. . .
[25] java.awt.EventDispatchThread.run (EventDispatchThread.java:100) -
Finally, this backtrace illustrates the invocation of a model method from the
update method of a view, in particular the
caltool.View.Lists.viewAppointmentsList method being invoked from the
ViewUI.AppintmentsListDisplay.update method.
-
In this case, update is called explicitly from the action listener
associated with the `View->Lists->Appointments' menu item.
- In upcoming examples of the observer/observable pattern, we'll see update called from the Java runtime, after a model or view class calls the Observable.notifyObservers method.
[1] caltool.view.Lists.viewAppointmentsList (Lists.java:60) [2] caltool.view_ui.AppointmentsListDisplay.update (AppointmentsListDisplay.java:79) [3] caltool.view_ui.ViewMenu$11.actionPerformed (ViewMenu.java:263) [4] javax.swing.AbstractButton.fireActionPerformed (AbstractButton.java:1,819)
. . .
[28] java.awt.EventDispatchThread.run (EventDispatchThread.java:100) -
In this case, update is called explicitly from the action listener
associated with the `View->Lists->Appointments' menu item.
-
For initial testing of a model/view design, it is very useful to have sample
model data, that are displayed in corresponding views.
-
In the beginning, these data can be entirely "canned", i.e., defined as
constants in the model classes.
- A good place to get concrete example data values is from the requirements.
-
In the beginning, these data can be entirely "canned", i.e., defined as
constants in the model classes.
-
The model data can be delivered to the view using the same methods that will
ultimately produce the real data.
-
For example, if an iterator method is used to access model data, the body of
the method can produce the canned data.
- If collection-valued data are returned by the model, canned data can be generated by temporary testing methods
-
For example, if an iterator method is used to access model data, the body of
the method can produce the canned data.
-
Examples of the preceding two forms of canned data generation are illustrated
in the Calendar Tool code from the Week 3 notes.
-
The iterator methods in the MonthlyAgenda model class deliver a fixed
month of data to the MonthlyAgendaDisplay view class.
- In the Lists model class, there is a generateSampleList() method that generates a sample data value that appears in the requirements; this piece of data is returned by Lists.viewAppointmentList() to the AppointmentsListDisplay view class.
-
The iterator methods in the MonthlyAgenda model class deliver a fixed
month of data to the MonthlyAgendaDisplay view class.
-
Team developers should design their individual packages and classes to be
testable independently from other team members' packages.
-
Providing "canned" test data is one aspect of independently testable designs.
-
Such test data are used when data-producing packages are not yet implemented by
other team members.
- These data can also be very handy when an implemented package unexpectedly breaks, leaving users of the package stuck until the broken package is fixed.
-
Such test data are used when data-producing packages are not yet implemented by
other team members.
-
In a Java-based implementation, having individualized main methods
supports independent testing.
-
For convenience, these mains can be in model classes.
-
During the initial phases of development, it's fine to have some testing done
directly in the model classes.
-
These initial tests are designed to check that an implementation is going in
the right direction.
- The initial tests will evolve into the formal tests that are in the testing project directory.
-
These initial tests are designed to check that an implementation is going in
the right direction.
-
For convenience, these mains can be in model classes.
-
A testing main method in a model class does the following steps:
-
Construct model class(es) to be tested.
-
Construct and compose companion view(s).
-
Construct canned test data.
- Show the top-level view(s).
-
Construct model class(es) to be tested.
- Independently-testable designs allow incremental development, meaning the implementation can be tested in successively refined increments, each with more strenuous and less canned test data.
-
The key packages we'll cover in these notes are:
-
java.lang -- the fundamental Java language package, with classes such as
Object, String, and System.
-
java.util -- the higher-level Java language package, including the
collection classes, date/time classes, and others.
- java.io -- file input/output and related processing.
-
java.lang -- the fundamental Java language package, with classes such as
Object, String, and System.
-
The functionality provided in these packages is central to the work you're
doing in 309.
-
The classes and interfaces in these packages are summarized in the UML diagrams
that follow.
-
Package java.lang

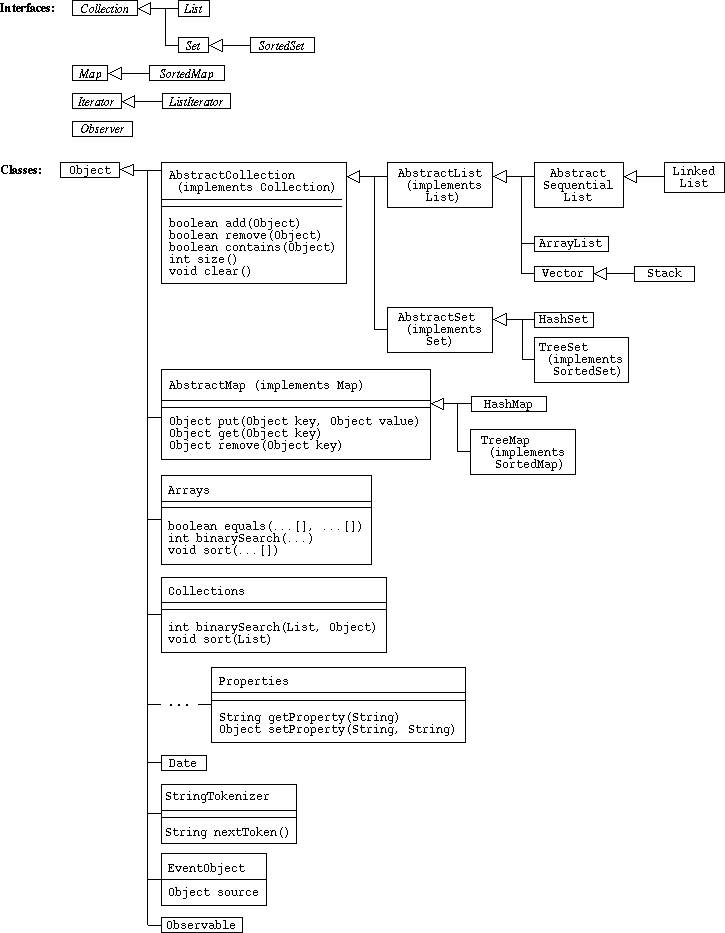
-
Package java.io
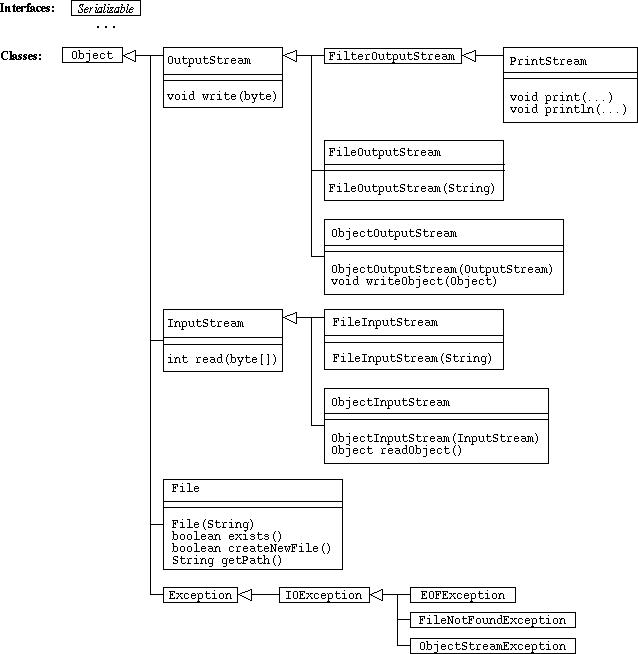
-
When the user enters data in a GUI, a View class collects it in raw form.
-
For example, the getText method extracts the string data from a
JTextField.
-
Once raw data are collected they are:
-
Converted by the model, from their raw view form into whatever form the model
needs, e.g., a string-to-numeric conversion.
-
Validated by the model, based on preconditions to a model processing method.
- Processed by the model as appropriate.
-
Converted by the model, from their raw view form into whatever form the model
needs, e.g., a string-to-numeric conversion.
-
There are a number of ways to perform input data validation in a model/view
design.
-
In general, most if not all of the validation should be done by the model.
-
In jargon terms, we have a "smart model and stupid view".
-
What this means is that the view does not know anything "smart" about the data,
in terms of its structure, or whether it's semantically valid.
-
The view is in charge of displaying data in the UI, and managing the
event-based interactions with the user.
- The model is in charge of storing the data, and managing all of the content-based access and manipulation of the data, including validation.
-
In jargon terms, we have a "smart model and stupid view".
-
In a design that includes formally-specified of methods, a useful way to handle
data validation is with exception handling
- This style of design is discussed in the next several points of the notes.
-
Normally, when a method is entered via a call, it exits by returning to the
caller.
-
In a language with an exception handling mechanism, there is an "abnormal" way
for a method to exit -- by throwing (a.k.a., raising) an exception.
-
Raising an exception allows a method to exit in a manner separate from
its normal return-to-caller mode.
-
When an exception is thrown in a method, control does not return directly to
the caller, but rather some other active method that catches (a.k.a.,
handles) the exception.
-
The catch can be in the immediate caller, but it is not limited to be.
- The catch does have to be performed by a currently active method; i.e., a method that directly or indirectly called the method in which the exception occurred.
-
Raising an exception allows a method to exit in a manner separate from
its normal return-to-caller mode.
-
Different programming languages provide different styles of exception handling,
and details differ widely between languages.
-
At the design level, we use an abstract graphical notation to depict exception
handling.
- At the implementation, we will use standard Java notation for exception handling.
-
At the design level, we use an abstract graphical notation to depict exception
handling.
-
In our high-level function diagram notation, exception handling is shown with
labeled arrows leading into and out from a method.
-
Figure 1 is an excerpt from the 309 handout on the
graphical modeling notation
which illustrates the exception diagramming format.
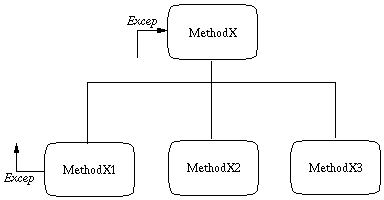
Figure 1: Event diagramming notation.
-
In the Figure, MethodX calls three submethods X1, X2, and
X3.
-
MethodX2 and MethodX2 return in the normal way.
- MethodX1 can return in the normal way, but also throw an exception that is caught by MethodX.
-
In the Figure, MethodX calls three submethods X1, X2, and
X3.
- This notation is used in the example diagrams that follow.
-
Figure 2 illustrates the use of exception handling to validate user input
data, in a Calendar Tool ScheduleEvent dialog.
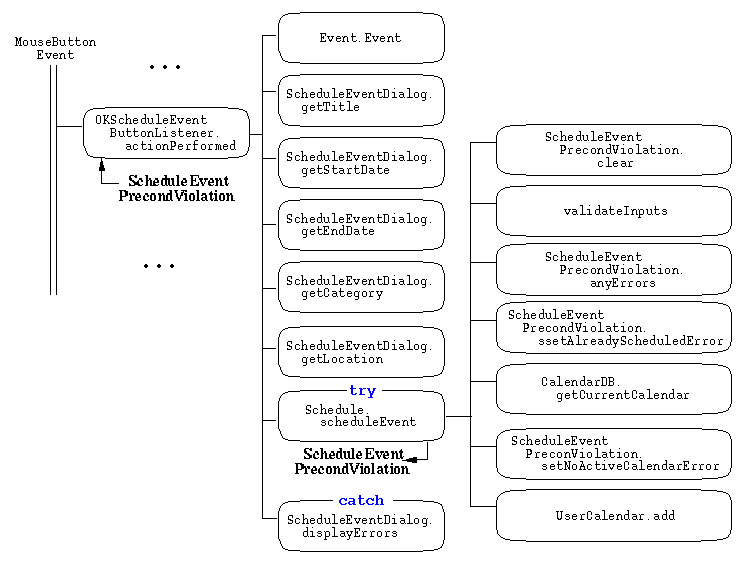
Figure 2: User input data collection and validation for scheduling an event.
-
The figure shows the model method Schedule.scheduleEvent throwing an
ScheduleEventPrecondViolation exception to the companion view method
OKScheduleEventButtonListener.actionPerformed.
-
The exception is thrown when one or more input errors is detected, based on the
processing done the the scheduleEvent method.
-
What follows is the code for
OKScheduleEventButtonListener.actionPerformed() and friends,
corresponding to the design shown in Figure 2.
public class OKScheduleEventButtonListener implements ActionListener { /** * Construct this with the given Schedule model and parent dialog view. * Access to the model is for calling its scheduleEvent method. Access to * the parent view is for gathering data to be sent to scheduleEvent. */ public OKScheduleEventButtonListener(Schedule schedule, ScheduleEventDialog dialog) { this.schedule = schedule; this.dialog = dialog; } /** * Respond to a press of the OK button by calling ScheduleEvent with a new * Event. The Event data are gathered from the JTextFields and JComboBox * in the parent dialog. */ public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { try { schedule.scheduleEvent( new caltool.schedule.Event( dialog.getTitle(), // Title as a string dialog.getStartDate(), // Start date as a Date dialog.getEndDate(), // Start date as a Date dialog.getCategory(), // Category as a Category dialog.getLocation() // Location as a string ) ); } catch (ScheduleEventPrecondViolation errors) { dialog.displayErrors(errors); } } /** The companion model */ protected Schedule schedule; /** The parent view */ protected ScheduleEventDialog dialog; }
-
Here is the code for companion model method that potentially throws the
exception.
public class Schedule extends Model { ... /** * ScheduleEvent adds the given Event to this.data, if an event of the same * time, duration, and title is not already scheduled. * <pre> pre: // // The Title field is not empty. // (event.title != null && event.title.length() >= 1) && // // The startOrDueDate field is a valid date value. // (event.startOrDueDate != null) && event.startOrDueDate.isValid() && // // If non-empty, the EndDate field is a valid date value. // if (event.endDate != null) event.endDate.isValid() && // // The current workspace is not null. // (calDB.getCurrentCalendar() != null) && // // No event of same startDate and title is in the current workspace // calendar. // // No event of same startDate and title is in the current calendar. // ! exists (ScheduledItem item ; calDB.getCurrentCalendar().items.contains(item) ; (item.startOrDueDate.equals(event.startOrDueDate)) && item.duration.equals(event.duration) && (item.title.equals(event.title))); post: // // If preconds met, a scheduled item is in the output calendar if // and only if it is the new appt to be added or it is in the // input calendar. // forall (ScheduledItem item; calDB'.getCurrentCalendar().items.contains(item) iff (item == event || calDB.getCurrentCalendar().items.contains(item))) && // // Also, requiresSaving is true in the output calendar. // calDB.getCurrentCalendar().requiresSaving; */ public void scheduleEvent(Event event) throws ScheduleEventPrecondViolation { /* * Clear out the error fields in precond violation exception object. */ scheduleEventPrecondViolation.clear(); /* * Throw a precond violation if the validly check fails on the start or * end date. */ if (validateInputs(event).anyErrors()) { throw scheduleEventPrecondViolation; } /* * Throw a precond violation if an event of the same start date and * title is already scheduled. */ if (alreadyScheduled(event)) { scheduleEventPrecondViolation.setAlreadyScheduledError(); throw scheduleEventPrecondViolation; } /* * Throw a precond violation if there is no currently active calendar. * Note that this condition will not be violated when interacting * through the view, since the 'Schedule Event' menu item is disabled * whenever the there is no active calendar. */ if (calDB.getCurrentCalendar() == null) { scheduleEventPrecondViolation.setNoActiveCalendarError(); throw scheduleEventPrecondViolation; } /* * If preconditions are met, add the given event to the currently * active calendar. */ calDB.getCurrentCalendar().add(event); } } -
Here is the code for the ScheduleEventPrecondViolation:
package caltool.schedule; import caltool.PrecondViolation; import java.util.*; /**** * * Class ScheduleEventPrecondViolation defines and exception containing error * conditions for the Schedule.scheduleEvent method. It contains a list of * the specific error messages that may be output in response to a precondition * having been violated by a call th scheduleEvent. * */ public class ScheduleEventPrecondViolation extends Exception implements PrecondViolation { /** * Construct this by initializing the error message list to an empty list, * initializing the numErrors count to 0, and initializing local copies of * the error message text for each of the possible errors from * Schedule.scheduleEvent. */ public ScheduleEventPrecondViolation() { errors = new ArrayList(); emptyTitleMessage = new String( "Event title cannot be empty."); invalidStartDateMessage = new String( "Invalid start date."); invalidEndDateMessage = new String( "Invalid end date."); noActiveCalendarMessage = new String( "There is no active calendar in the Calendar Tool workspace."); alreadyScheduledMessage = new String( "An event of the given start date and title is already scheduled."); numErrors = 0; } /*-* * Implemented interface methods. */ /** * Return the error list. */ public String[] getErrors() { return (String[]) errors.toArray(new String[1]); } /** * Clear all error messages. */ public void clear() { errors = new ArrayList(); numErrors = 0; } /** * Return true if any errors have been set. */ public boolean anyErrors() { return (numErrors > 0); } /** * Return the number of errors. */ public int numberOfErrors() { return numErrors; } /*-* * Error-setting methods */ /** * Set the already scheduled error message. */ public void setAlreadyScheduledError() { errors.add(alreadyScheduledMessage); numErrors++; } /** * Set the invalid start date error message. */ public void setInvalidStartDateError() { errors.add(invalidStartDateMessage); numErrors++; } /** * Set the invalid end date error message. */ public void setInvalidEndDateError() { errors.add(invalidEndDateMessage); numErrors++; } /** * Set the no active calendar error message. */ public void setNoActiveCalendarError() { errors.add(noActiveCalendarMessage); numErrors++; } /*-* * Data fields */ /** List of current error messages */ protected ArrayList errors; /** Error message count */ protected int numErrors; /** Error message for event of same date,title already scheduled */ protected String alreadyScheduledMessage; /** Error message for invalid start date */ protected String invalidStartDateMessage; /** Error message for invalid end date */ protected String invalidEndDateMessage; /** Error message for no currently active calendar in the workspace */ protected String noActiveCalendarMessage; }
-
Finally, here is the code for the general interface that all precondition
violation exceptions must implement:
package caltool; /**** * * Interface PrecondViolation defines the methods that all precondition * violation exceptions must implement. * */ public interface PrecondViolation { /** * Return the concrete error list for precondition violation. Each * position in the list corresponds to violation of a particular * precondition clause. */ public String[] getErrors(); /** * Clear out all of the error messages in this. */ public void clear(); /** * Return true if one or more error messages has been set. */ public boolean anyErrors(); /** * Return the number of error messages. */ public int numberOfErrors(); }
-
Consider the Calendar Tool view for an individual scheduled item versus a
monthly view of items.
-
In the case of a single item view, the display shows data that are persistently
stored within the model data.
- In the case of a monthly view, some of the data are persistently stored, but the other parts of the data, in particular the month/day layout, are dynamically computed.
-
In the case of a single item view, the display shows data that are persistently
stored within the model data.
- These are examples of a data persistence design pattern we'll discuss further in upcoming lectures.