

Figure 2.2.1a: eHTML Classic Numbering syntax and its result.
The EClass application uses its own proprietary eHTML format to save lectures. eHTML is a markup language based upon HTML. Many of the tags used in HTML 4.01 are valid tags in eHTML. The following tags are invalid in eHTML:
A commonly used tag are the list tags. These include both the ordered lists <ol> and unordered lists <ul>. Lists provide the heirarchial structure that the lecture builds upon. The standard list attributes can be used to provide bulleted, alphanumeric, or roman numeral lists (See the W3C standard for details). Figure 2.2.1a shows both the eHTML syntax and result of alphanumeric and roman numeral lists (also referred to as "Classic Numbering"). Figure 2.2.1b shows the eHTML syntax and result for bulleted lists.


Figure 2.2.1a: eHTML Classic Numbering syntax and its result.


Figure 2.2.1b: eHTML bulleted list syntax and its result.
In addition, eHTML provides one more type value for <ol>
tags. This type is dewey. It utilizes the dewey decimal
system. Subsequently nested <ol> tags will also be dewey unless
specified otherwise. Figure 2.2.1c below shows an example of both eHTML dewey
decimal list syntax and its result.


Figure 2.2.1c: eHTML dewey syntax and its result.
Like the other <ol> types, the dewey type can be used with the
start attribute. The start attribute still accepts
integer values only. It is used to mark a different starting value for the
current hierarchical level. For example, if a top level dewey <ol> tag
has a start value of 3 and another dewey <ol> tag one level
lower has a start value of 4, then the second level would be 3.4
instead of 1.1 as it normally is. Only the hierarchical level with a
start value is altered, all other levels are unaffected. The
following illustration shows the eHTML that embodies this, and its result.
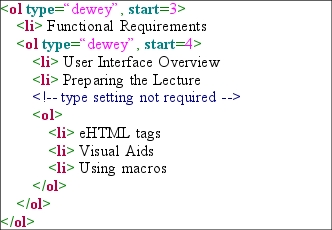

Figure 2.2.1d: eHTML dewey start syntax and
its result.
The <ol> and <ul> tags are also foldable points during the presentation. Every list topic can be expanded or collapsed in continuous mode (see 2.3.4.1. Continuous Mode). For example, in the eHTML in Figure 2.2.1c, "<ol>" line after the comment is a foldable point. Upon collapsing this point, all enclosed list items are hidden. In this example, "eHTML tags", "Visual Aids", and "Using macros" would all be hidden.